
Exploring Mechanical Energies in Simple Harmonic Motion
Interactive Video
•
Science
•
6th - 10th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
+1
Standards-aligned
Jackson Turner
FREE Resource
Standards-aligned
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
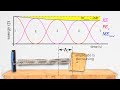
At which positions is the displacement of the mass equal to the amplitude?
Position 1 and 2
Position 2 and 3
Position 1 and 3
Position 1 and 4
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS4-1
NGSS.HS-PS4-3
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the velocity of the mass at positions 1 and 3?
Maximum
Zero
Minimum
Constant
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why is the kinetic energy zero at positions 1 and 3?
Because the velocity is zero
Because the mass is at rest
Because the displacement is zero
Because the acceleration is zero
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS3-1
NGSS.HS-PS3-2
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the relationship between velocity and kinetic energy?
Kinetic energy is directly proportional to velocity
Kinetic energy is inversely proportional to the square of velocity
Kinetic energy is inversely proportional to velocity
Kinetic energy is directly proportional to the square of velocity
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
At which position does the elastic potential energy have its maximum value?
Positions 1 and 3
Position 2
Position 3
Position 1
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why is the elastic potential energy zero at position 2?
Because the spring constant is zero
Because the acceleration is zero
Because the velocity is zero
Because the displacement from equilibrium is zero
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does the horizontal line representing the total mechanical energy indicate?
The total mechanical energy is zero
The total mechanical energy is constant
The total mechanical energy is decreasing
The total mechanical energy is increasing
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Popular Resources on Wayground

8 questions
Spartan Way - Classroom Responsible
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

14 questions
Boundaries & Healthy Relationships
Lesson
•
6th - 8th Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

3 questions
Integrity and Your Health
Lesson
•
6th - 8th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

9 questions
FOREST Perception
Lesson
•
KG

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade
Discover more resources for Science

22 questions
Phases of the moon
Quiz
•
8th Grade

20 questions
Rocks and The Rock Cycle
Quiz
•
6th Grade

20 questions
Flow of Energy
Quiz
•
7th Grade

20 questions
Waves and Wave Properties
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

8 questions
Amoeba Sister Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction
Interactive video
•
8th Grade

10 questions
Exploring the Rock Cycle: Types and Formation
Interactive video
•
6th - 8th Grade

16 questions
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Review
Quiz
•
7th Grade

20 questions
8th Grade Science STAAR Review
Quiz
•
8th Grade