What is the basic construction of a DC motor?
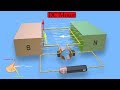
DC Motor Mechanics and Principles
Interactive Video
•
Ethan Morris
•
Physics, Science
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
A current-carrying armature connected directly to the battery.
A rotating coil connected to an AC supply.
A stationary coil connected to an AC supply.
A current-carrying armature connected to the supply through commutator segments and brushes.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens when a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field?
It stops conducting current.
It experiences a mechanical force.
It becomes magnetized.
It generates heat.
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the elementary model of a DC motor, what is the direction of current in the left-side conductor?
Inward
Upward
Outward
Downward
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How can the direction of mechanical force be determined in a DC motor?
By measuring the voltage.
By using the right-hand rule.
By using Fleming's left-hand rule.
By observing the rotation direction.
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does the thumb indicate in Fleming's left-hand rule?
Direction of mechanical force.
Direction of magnetic field.
Direction of voltage.
Direction of current.
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the turn when it comes to a vertical position in respect to the magnetic field?
The current decreases.
The current increases.
There is no current in the conductor.
The conductor heats up.
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What causes the turn to continue rotating even when there is no current?
Friction.
Magnetic force.
Electrical resistance.
Moment of inertia.
8.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the direction of mechanical force on the conductor near the South Pole?
Outward
Downward
Upward
Inward
9.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the direction of mechanical force on the conductor near the North Pole?
Upward
Downward
Outward
Inward
10.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How does a practical DC motor differ from the elementary model?
It has a stationary armature.
It does not use commutator segments.
It uses AC supply instead of DC.
It has multiple turns on the armature coil and multiple poles.
Explore all questions with a free account
Similar Resources on Quizizz

4 questions
Electric Motor: How Current and Magnetic Fields Cause Rotation
Interactive video
•
10th Grade - University

11 questions
Electromagnetism Concepts and Applications
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding DC Motors and Their Components
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Understanding DC Motor Components
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding DC Motors and Their Functions
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

8 questions
Electric Motor: How Current and Magnetic Fields Cause Rotation
Interactive video
•
10th Grade - University

8 questions
Understanding Fleming's Left Hand Rule and the Motor Effect
Interactive video
•
10th Grade - University

8 questions
Electric Generator
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Quizizz

17 questions
CAASPP Math Practice 3rd
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
math review
Quiz
•
4th Grade

21 questions
6th Grade Math CAASPP Practice
Quiz
•
6th Grade

13 questions
Cinco de mayo
Interactive video
•
6th - 8th Grade

20 questions
Reading Comprehension
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Types of Credit
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
4th Grade Math CAASPP (part 1)
Quiz
•
4th Grade

45 questions
5th Grade CAASPP Math Review
Quiz
•
5th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

45 questions
Physics Semester 2 Review
Quiz
•
11th Grade

52 questions
AP Physics 1 Review
Quiz
•
11th Grade

50 questions
Physics semester 2 review
Quiz
•
11th Grade

40 questions
Light and EM Waves
Quiz
•
11th - 12th Grade

7 questions
EOY REVIEW 4
Lesson
•
10th - 12th Grade

82 questions
Physics Final Review
Quiz
•
11th Grade

20 questions
Electricity/Magnets
Quiz
•
9th Grade

40 questions
Physics Semester 1 Final Review
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade