Kinematics and Vector Quantities
Interactive Video
•
Physics, Science
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Jackson Turner
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does kinematics primarily describe?
The energy of moving objects
The forces acting on objects
How objects move with reference to force
How objects move without reference to force
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following is a vector quantity?
Mass
Distance
Displacement
Temperature
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How is displacement different from distance?
Both are vector quantities
Both are scalar quantities
Distance includes direction, displacement does not
Displacement includes direction, distance does not
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
If a person travels 15 meters east, what are they describing?
Speed
Distance
Displacement
Velocity
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the main difference between speed and velocity?
Speed is a vector, velocity is a scalar
Both are vector quantities
Speed has direction, velocity does not
Velocity includes direction, speed does not
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How do you calculate average speed?
Velocity divided by time
Displacement divided by time
Final position minus initial position
Distance divided by time
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
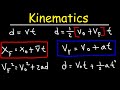
Which formula is used for objects moving with constant speed?
v^2 = u^2 + 2as
s = ut + 1/2 at^2
v = u + at
d = vt
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

8 questions
7 enigmas de la ciencia
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Air Pollution and Exercise Quiz
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Exploring Earth, Sun, and Moon: the Sun
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Human Anatomy: Neurons and the Nervous System
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Percentage Yield
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Dielectrics in Capacitors
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Gene Regulation and the Lac Operon
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

5 questions
This is not a...winter edition (Drawing game)
Quiz
•
1st - 5th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

10 questions
Identify Iconic Christmas Movie Scenes
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Christmas Trivia
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

18 questions
Kids Christmas Trivia
Quiz
•
KG - 5th Grade

11 questions
How well do you know your Christmas Characters?
Lesson
•
3rd Grade

14 questions
Christmas Trivia
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
How the Grinch Stole Christmas
Quiz
•
5th Grade