AP Chemistry Acid Base Basics
Quiz
•
Chemistry
•
11th - 12th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Standards-aligned

Charles Martinez
Used 1+ times
FREE Resource
Enhance your content in a minute
15 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
15 mins • 1 pt

A buffer solution is prepared by mixing equal volumes of 0.50 M weak acid with 1.0 M of its conjugate base. Based on the data given in the table above, which of the following pairs of chemical solutions should be used to prepare the buffer solution so that the pH will be between 4 and 7?
CH3COOH and NH3
CH3COOH and CH3COONa
H2CO3 and NH3
H2CO3 and Na2CO3
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
15 mins • 1 pt
Ascorbic acid, H2C6H6O6(s), is a diprotic acid with K1 = 7.9 × 10–5 and K2 = 1.6 × 10–12. In a 0.005 M aqueous solution of ascorbic acid, which of the following species is present in the lowest concentration?
H3O+(aq)
H2C6H6O6(aq)
HC6H6O6-(aq)
C6H6O62-(aq)
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
15 mins • 1 pt
In the titration of a weak acid of unknown concentration with a standard solution of a strong base, a pH meter was used to follow the progress of the titration. Which of the following is true for this experiment?
The [H+] at the equivalence point equals the ionization constant of the acid.
The pH at the equivalence point depends on the indicator used.
The graph of pH versus volume of base added rises gradually at first and then much more rapidly.
The graph of pH versus volume of base added shows no sharp rise.
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
15 mins • 1 pt
Which of the following is the correct equilibrium expression for the hydrolysis of CO3 2– ?
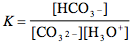
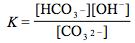
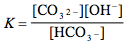
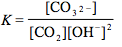
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
15 mins • 1 pt

Which of the following best approximates the Ka value for this weak acid?
1 x 10–3
1 x 10–4
1 x 10–5
1 x 10–6
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
15 mins • 1 pt

Which point on the titration curve corresponds to the point at which the moles of the added strong base are equal to the moles of the weak acid initially present?
Q
R
S
T
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
15 mins • 1 pt

At point P in the titration, which of the following species has the highest concentration?
HA
A–
H3O+
OH–
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
VESPR Grade 10as
Quiz
•
11th - 12th Grade

13 questions
Metallic solids
Quiz
•
12th Grade

15 questions
ÔN TẬP GK II HÓA 11 -P3
Quiz
•
11th Grade

20 questions
Isomer dan Reaksi-reaksi senyawa turunan alkana
Quiz
•
12th Grade

10 questions
Volumetric Analysis 2
Quiz
•
10th - 11th Grade

10 questions
ASESMEN DIAGNOSTIK KOGNITIF KELAS XI
Quiz
•
11th Grade

20 questions
Kuis Asam Basa
Quiz
•
11th Grade

20 questions
Stopień utlenienia
Quiz
•
6th Grade - University
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

54 questions
Analyzing Line Graphs & Tables
Quiz
•
4th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
4th Grade
Discover more resources for Chemistry

20 questions
Types of Chemical Reactions
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
electron configurations and orbital notation
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

5 questions
Mole Conversions Made Easy
Interactive video
•
11th Grade

10 questions
16. Limiting Reagent/% Yield Practice
Quiz
•
11th Grade

20 questions
Metric Conversions
Quiz
•
11th Grade

10 questions
PERIODIC TRENDS
Quiz
•
11th Grade

14 questions
Reaction Types, Balancing, and Predicting Products
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

8 questions
Empirical and Molecular Formulas
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade