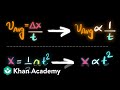
Understanding NASA's Mars Mission Planning
Interactive Video
•
Mathematics, Physics, Science
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Emma Peterson
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is one of the main challenges NASA faces in planning a mission to Mars?
Training astronauts for zero gravity
Managing fuel, oxygen, and radiation exposure
Calculating the exact distance to Mars
Finding a suitable landing spot
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What assumptions are made in the simplified model for the Mars mission?
Variable acceleration and initial velocity
Circular trajectory and constant speed
Variable speed and changing direction
Constant acceleration and zero initial velocity
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why is it important to choose the right mathematical model when comparing average velocities?
To avoid using complex equations
To make the calculations simpler
To accurately reflect the relationship between variables
To ensure the model is easy to understand
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the mission scenarios discussed, how does halving the travel time affect the average velocity?
It remains the same
It triples
It doubles
It halves
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the relationship between acceleration and time in the mission scenarios?
Acceleration is inversely proportional to the square of time
Acceleration is independent of time
Acceleration is directly proportional to the square of time
Acceleration is directly proportional to time
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why is an acceleration of 40 m/s² considered too high for human travel in space?
It exceeds the safe limits for prolonged human exposure
It would require too much fuel
It would make communication with Earth difficult
It would cause the spacecraft to overheat
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the third mission scenario, how does increasing travel time by 50% affect the distance traveled?
The distance more than doubles
The distance increases by 50%
The distance remains the same
The distance decreases
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Forest Self-Management
Lesson
•
1st - 5th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

30 questions
Thanksgiving Trivia
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

30 questions
Thanksgiving Trivia
Quiz
•
6th Grade

11 questions
Would You Rather - Thanksgiving
Lesson
•
KG - 12th Grade

48 questions
The Eagle Way
Quiz
•
6th Grade

10 questions
Identifying equations
Quiz
•
KG - University

10 questions
Thanksgiving
Lesson
•
5th - 7th Grade
Discover more resources for Mathematics

10 questions
Identifying equations
Quiz
•
KG - University

20 questions
Pythagorean Theorem and Their Converse
Quiz
•
8th - 9th Grade

20 questions
Is it a Function?
Quiz
•
8th - 9th Grade

18 questions
Scatterplot Associations
Quiz
•
7th - 9th Grade

26 questions
Intro to Exponential Functions
Quiz
•
9th Grade

8 questions
211 - Write Equation Given Two Points
Quiz
•
9th Grade

16 questions
Solving Systems Review
Quiz
•
9th Grade

18 questions
Triangle Similarity Review
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade