
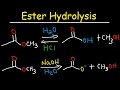
Acid and Base Catalysis Concepts
Interactive Video
•
Chemistry, Science
•
10th Grade - University
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Ethan Morris
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What are the products when methyl acetate reacts with water and HCl under acidic conditions?
Carboxylic acid and methanol
Acetic acid and ethanol
Ethanol and acetic acid
Methanol and ethyl acetate
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the acid-catalyzed ester hydrolysis, which ion is formed when HCl is added to water?
Na+
H3O+
Cl-
OH-
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
During the acid-catalyzed mechanism, which oxygen in the ester is more likely to be protonated?
The oxygen with no charge
The oxygen with a negative formal charge
The oxygen bonded to carbon
The oxygen with a positive formal charge
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the role of water in the acid-catalyzed ester hydrolysis mechanism?
Acts as a weak base
Acts as a strong acid
Acts as a nucleophile
Acts as a catalyst
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the final product of the acid-catalyzed ester hydrolysis?
Ester
Methanol
Deprotonated carboxylic acid
Protonated carboxylic acid
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the base-catalyzed mechanism, what is the role of hydroxide?
Acts as a catalyst
Acts as an acid
Acts as a solvent
Acts as a nucleophile
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to methoxide in the base-catalyzed ester hydrolysis?
It acts as a nucleophile
It forms a double bond
It attacks the carbonyl carbon
It deprotonates the carboxylic acid
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

6 questions
Los vecinos más cercanos de la Tierra: el planeta hermano de la Tierra
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

6 questions
IIT/JEE Chemistry Practice #6: Stoichiometry/Precipitation Reactions
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

11 questions
Organic Chemistry Synthesis Concepts
Interactive video
•
10th Grade - University

10 questions
Enzyme Cofactors and Functions
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Energy Resources and Their Advantages and Disadvantages
Interactive video
•
10th Grade - University

8 questions
Water Pollution
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

8 questions
Heterocycles Part 2: Pyridine
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

8 questions
Organic Chemistry Synthesis Challenge 4
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

29 questions
Alg. 1 Section 5.1 Coordinate Plane
Quiz
•
9th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

11 questions
FOREST Effective communication
Lesson
•
KG

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade
Discover more resources for Chemistry

22 questions
Unit 9 Gas Law Quiz
Quiz
•
10th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Types of Chemical Reactions
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Types of Chemical Reactions
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Acids and Bases
Quiz
•
10th Grade

7 questions
GCSE Chemistry - Balancing Chemical Equations #4
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Chemistry: Classification of Matter
Quiz
•
10th Grade

40 questions
Unit 3 (Part 1) Chemical Equations & Reactions Review Game
Quiz
•
8th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Stoichiometry Review
Quiz
•
10th Grade