Metal-Ligand Interactions and Coordinate Bonds
Interactive Video
•
Chemistry, Science
•
10th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Emma Peterson
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is a key characteristic of a coordinate covalent bond?
Atoms share electrons equally.
One atom donates both electrons for the bond.
Both atoms donate one electron each.
Electrons are transferred completely.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In a regular covalent bond between two bromine atoms, how many electrons does each atom contribute?
One electron
Two electrons
Three electrons
No electrons
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
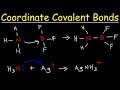
Why is the bond between nitrogen and boron in ammonia and boron trifluoride considered a coordinate covalent bond?
Both atoms share electrons equally.
Nitrogen donates both electrons for the bond.
Boron donates both electrons for the bond.
Electrons are transferred from boron to nitrogen.
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What role does ammonia play in the reaction with boron trifluoride?
Neutral molecule
Electron acceptor
Lewis base
Lewis acid
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the metal-ligand interaction example, what is the charge of the silver cation?
Variable
Positive
Neutral
Negative
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the coordination number in the complex ion formed with ammonia and silver?
One
Two
Three
Four
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What type of interaction is involved in forming a complex ion with a metal and ligands?
Van der Waals forces
Hydrogen bonding
Metal-ligand interaction
Ionic interaction
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

8 questions
EPA announces new rules to limit toxic ‘forever chemicals’ in drinking water
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

6 questions
Landmarks - Lake Titicaca
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

6 questions
VOICED: Libya's Jibril meets NATO's Rasmussen in Brussels
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

8 questions
Moore's Law and The Secret World Of Ones And Zeroes
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

8 questions
How Atomic Physics Started
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Ice Breaker Trivia: Food from Around the World
Quiz
•
3rd - 12th Grade

20 questions
MINERS Core Values Quiz
Quiz
•
8th Grade

10 questions
Boomer ⚡ Zoomer - Holiday Movies
Quiz
•
KG - University

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

20 questions
Multiplying and Dividing Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

10 questions
How to Email your Teacher
Quiz
•
Professional Development

15 questions
Order of Operations
Quiz
•
5th Grade
Discover more resources for Chemistry

20 questions
Physical or Chemical Change/Phases
Quiz
•
8th Grade - University

19 questions
Lewis Dot Structures -Review and Master
Quiz
•
10th Grade

10 questions
Electron Configuration, Orbital Notation, & Dot diagrams
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Intro to Atoms Vocabulary Quiz
Quiz
•
8th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Naming Polyatomic Ionic compounds
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

45 questions
Unit 3: Atomic Assault Summative Review
Quiz
•
11th Grade

16 questions
Electron Configurations, and Orbital Notations
Quiz
•
9th - 11th Grade

17 questions
Periodic Trends
Quiz
•
10th Grade