
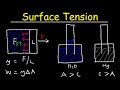
Understanding Surface Tension
Interactive Video
•
Physics, Chemistry, Science
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Emma Peterson
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What shape does water form on a surface due to surface tension?
Spherical droplets
Cubic
Pyramidal
Flat sheet
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why can a steel needle float on water despite being denser?
It is lighter than water
Surface tension supports it
It is magnetic
Water repels steel
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What causes the net downward force on water molecules at the surface?
Adhesive forces
Gravitational pull
Cohesive forces
Wind pressure
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the Greek symbol used to represent surface tension?
Beta
Delta
Alpha
Gamma
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How is surface tension quantified in terms of physics variables?
Density per unit length
Force per unit length
Force per unit volume
Mass per unit area
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the surface tension of water as temperature increases?
It decreases
It increases
It remains constant
It fluctuates
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
At 100 degrees Celsius, what is the surface tension of water?
0.076 N/m
0.072 N/m
0.059 N/m
0.080 N/m
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Understanding the Continuity Equation
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Milling Machine Concepts and Applications
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Exploration and Discovery in Astronomy
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Surface Area and Integration Techniques
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Multidisciplinary Approaches in Genetic Research
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Exploring Earth, Sun, and Moon: Earth's Moon
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Oceanography: Ocean Temperature, Pressure, and Density
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding the Sun: A Celestial Journey
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

29 questions
Alg. 1 Section 5.1 Coordinate Plane
Quiz
•
9th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

11 questions
FOREST Effective communication
Lesson
•
KG

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

10 questions
Exit Check 4.1 - Destructive Processes
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Exit Check 4.2 - Constructive Forces
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Exit Check 4.3 - Conservation of Momentum
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Exit Check 4.4 - Momentum Calculations
Quiz
•
9th Grade

21 questions
EM Spectrum
Quiz
•
6th - 9th Grade

20 questions
Simple Machines and Mechanical Advantage Quiz
Quiz
•
9th Grade

14 questions
Graphs of Motion, Velocity & Acceleration
Quiz
•
8th - 9th Grade

21 questions
PE & KE Practice
Quiz
•
8th - 11th Grade