What is the main difference between cis and trans isomers?
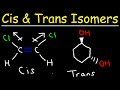
Cis and Trans Isomerism Concepts
Interactive Video
•
Ethan Morris
•
Chemistry, Science
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Cis isomers are always nonpolar, trans are always polar.
Cis isomers have groups on the same side, trans have them on opposite sides.
Cis isomers have higher melting points than trans isomers.
Cis isomers have groups on opposite sides, trans have them on the same side.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why does the cis isomer have a higher boiling point than the trans isomer?
Because it is nonpolar.
Because it has a higher molecular weight.
Because it is polar and has a net dipole moment.
Because it has more hydrogen bonds.
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following is true about the dipole moment of trans isomers?
They have a dipole moment of approximately three dbi.
They have a higher dipole moment than cis isomers.
They have a dipole moment only in polar solvents.
They always have a dipole moment of zero.
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the boiling point of the cis isomer mentioned in the video?
37 degrees Celsius
47.5 degrees Celsius
60 degrees Celsius
100 degrees Celsius
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is required to convert a trans isomer to a cis isomer?
Breaking the pi bond.
Adding more hydrogen atoms.
Breaking the sigma bond.
Increasing the temperature slightly.
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the energy barrier for rotation in ethane compared to cis and trans isomers?
The same in both.
Higher in ethane.
Lower in ethane.
Non-existent in ethane.
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How can cis and trans isomers be represented using rings?
By using wedges and dashes to show direction.
By using different colors for each group.
By drawing them as linear structures.
By placing all groups in the same plane.
8.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the context of cis and trans isomers, what does a wedge represent?
A group going into the page.
A group coming out of the page.
A group on the same plane as the page.
A group that is nonpolar.
9.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What determines if an alkene can show cis and trans isomerism?
The presence of a triple bond.
The presence of different groups on each carbon of the double bond.
The presence of identical groups on the same carbon.
The presence of a single bond.
10.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why can't an alkene with identical groups on the same carbon show cis and trans isomerism?
Because it lacks a double bond.
Because it has free rotation.
Because it doesn't have different groups on each carbon of the double bond.
Because it is always nonpolar.
Explore all questions with a free account
Similar Resources on Quizizz

11 questions
Cis-Trans Isomerism and IUPAC Nomenclature
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Naming and Identifying Cycloalkanes
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Chair Conformations and Stability
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Practice Problem: E2 on Cyclic Systems and Cyclohexane Chairs
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

11 questions
Isomerism and Its Biological Implications
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Alkene Nomenclature and Isomerism
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Stereoisomerism: Unlocking the Secrets of Molecular Twins
Interactive video
•
10th Grade - University

11 questions
Understanding Isomers
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Quizizz

17 questions
CAASPP Math Practice 3rd
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
math review
Quiz
•
4th Grade

21 questions
6th Grade Math CAASPP Practice
Quiz
•
6th Grade

13 questions
Cinco de mayo
Interactive video
•
6th - 8th Grade

20 questions
Reading Comprehension
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Types of Credit
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
4th Grade Math CAASPP (part 1)
Quiz
•
4th Grade

45 questions
5th Grade CAASPP Math Review
Quiz
•
5th Grade
Discover more resources for Chemistry

20 questions
Types of Chemical Reactions
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Acids and Bases
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Stoichiometry Practice
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Balancing Chemical Equations
Quiz
•
9th - 11th Grade

20 questions
Balancing Chemical Equations and Types of Reactions
Quiz
•
10th Grade

24 questions
Types of Chemical Reactions
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Stoichiometry Practice Quiz
Quiz
•
10th Grade

47 questions
Thermochemistry Review
Quiz
•
10th Grade