
Pythagorean Models
Authored by Anthony Clark
Mathematics
8th Grade
CCSS covered

AI Actions
Add similar questions
Adjust reading levels
Convert to real-world scenario
Translate activity
More...
Content View
Student View
18 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt
1. When three squares are joined at their vertices to form a right triangle, the combined area of the two smaller squares is the same as the area of the larger square.
Which three squares do NOT support this statement?
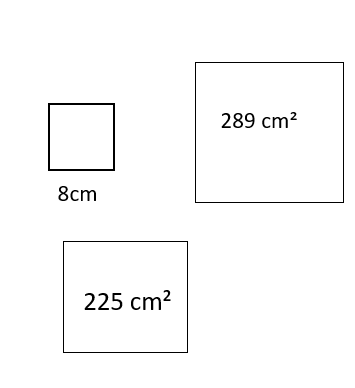
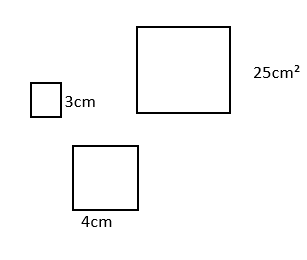
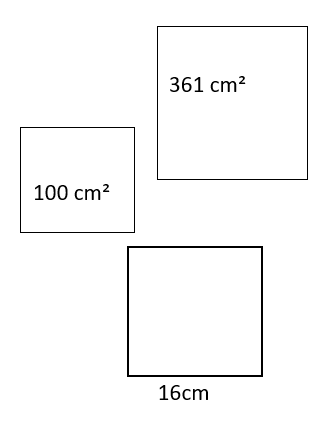
Tags
CCSS.8.G.B.8
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt

A teacher is showing his student Jacob to join three squares at their vertices to create the figure shown in the diagram. The student will use small congruent square tiles to cover each region without any gaps or overlaps. Based on the information, which statement is true?
The number of tiles needed to cover Square R is the same as the number of square tiles needed to cover Square G and Square M
The number of tiles needed to cover Square G is the same as the number of tiles needed to cover both Square R and Square M.
The number of tiles needed to cover Square M is the same as the number of square tiles needed to cover Square R and Square G.
Tags
CCSS.3.MD.C.5A
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt
The legs of a right triangle are represented by a and b, and the hypotenuse of the right triangle is represented by c. Which equation represents the Pythagorean Theorem?
a2 + b2 = c2
a2 + c2 = b2
a + b = c
Tags
CCSS.8.G.B.8
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt
The Pythagorean Theorem ONLY works on which triangle?
obtuse
scalene
isosceles
right
Tags
CCSS.8.G.B.8
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 1 pt

Which of the following sentences would belong in the proof that describes this image?
The sum of the areas of the two smaller squares is equal to the area of the large square.
The sum of the side lengths of the two smaller squares is equal to the side length of the large square.
The difference of the areas of the two smaller squares is equal to the area of the large square.
The differences of the side lengths of the two smaller squares is equal to the side length of the large square.
Tags
CCSS.8.G.B.8
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 4 pts

Which Pythagorean Triple does the picture illustrate?
4, 5, 6
2, 3, 4
3, 4, 5
1, 2, 3
Tags
CCSS.8.G.B.8
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
1 min • 4 pts

All of the a square plus all of the b square will perfectly fill the c square with nothing left over.
True
False
Tags
CCSS.8.G.B.8
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

20 questions
Decimals & Fractions
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

13 questions
Unit 8 Test Corrections
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Basic Math (M32102)
Quiz
•
10th - 11th Grade

20 questions
G12_Math+for+Bus+Eco_Term+Exam_Mock+Test
Quiz
•
12th Grade

15 questions
Quiz on module-03
Quiz
•
University

20 questions
Real Life Graphs
Quiz
•
8th Grade

20 questions
Pythagorean Theorem Practice
Quiz
•
7th - 9th Grade

19 questions
REVISION: DATA DESCRIPTION
Quiz
•
11th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

54 questions
Analyzing Line Graphs & Tables
Quiz
•
4th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
4th Grade
Discover more resources for Mathematics

14 questions
finding slope from a graph
Quiz
•
8th Grade

20 questions
Laws of Exponents
Quiz
•
8th Grade

12 questions
8th U5L9 Linear Models
Quiz
•
8th Grade

20 questions
Graphing Inequalities on a Number Line
Quiz
•
6th - 9th Grade

20 questions
Volume of cylinders, Cones and Spheres
Quiz
•
8th Grade

20 questions
One Step equations addition and subtraction
Quiz
•
5th - 8th Grade

20 questions
Mean, Median, Mode, and Range
Quiz
•
8th Grade

15 questions
Volume of a Cylinder
Quiz
•
8th Grade


