
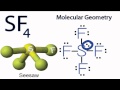
VSEPR Theory and Molecular Geometry
Interactive Video
•
Chemistry
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Lucas Foster
FREE Resource
Read more
6 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the initial assumption about the molecular geometry of SF4 based on its structure?
Octahedral
Trigonal Planar
Tetrahedral
Linear
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why does the presence of a lone pair of electrons affect the molecular geometry of SF4?
It changes the charge of the molecule.
It repels other atoms, altering the shape.
It has no effect on the geometry.
It attracts other atoms closer.
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
According to VSEPR Theory, what causes atoms and lone pairs to push apart in a molecule?
Electron pair repulsion
Nuclear attraction
Gravitational pull
Magnetic forces
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the role of VSEPR Theory in determining molecular geometry?
It predicts the color of molecules.
It explains the repulsion between electron pairs.
It calculates the energy levels of electrons.
It determines the mass of molecules.
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the actual molecular geometry of SF4?
Square Planar
Seesaw
Trigonal Bipyramidal
Tetrahedral
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why is SF4 considered a 'poster child' for a particular molecular geometry?
It has the highest number of lone pairs.
It perfectly exemplifies the seesaw shape.
It is the most common molecule.
It is the simplest molecule to study.
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

2 questions
Algebra 10 - The Cartesian Coordinate System
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

4 questions
Centroid Example Problem Using the Subtractive Method
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

8 questions
GCSE Maths - Congruent Triangle Rules #103
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

8 questions
CLEAN : Putin reforms reveal chasm between Russian generations
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
GCSE Secondary Maths Age 13-17 - Algebra: Pythagorous Theorem - Explained
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

2 questions
Calculating Surface Area and Volume of Cylinders
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

2 questions
GCSE Secondary Maths Age 13-17 - Geometry & Measures: Construction Lines - Explained
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Given the initial and terminal point, write the vector in component form
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

29 questions
Alg. 1 Section 5.1 Coordinate Plane
Quiz
•
9th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

11 questions
FOREST Effective communication
Lesson
•
KG

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade
Discover more resources for Chemistry

22 questions
Unit 9 Gas Law Quiz
Quiz
•
10th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Types of Chemical Reactions
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Types of Chemical Reactions
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Acids and Bases
Quiz
•
10th Grade

30 questions
Energy Review
Quiz
•
9th Grade

7 questions
GCSE Chemistry - Balancing Chemical Equations #4
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Chemistry: Classification of Matter
Quiz
•
10th Grade

40 questions
Unit 3 (Part 1) Chemical Equations & Reactions Review Game
Quiz
•
8th - 12th Grade