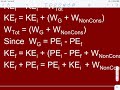
The Law of Conservation of Energy Explained
Interactive Video
•
Science
•
6th - 10th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Standards-aligned
Ethan Morris
FREE Resource
Standards-aligned
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary difference between conservative and non-conservative forces?
Non-conservative forces always increase mechanical energy, while conservative forces always decrease it.
Conservative forces always increase mechanical energy, while non-conservative forces always decrease it.
Non-conservative forces can store and release energy equally, while conservative forces cannot.
Conservative forces can store and release energy equally, while non-conservative forces cannot.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following is an example of a non-conservative force?
Static electricity
Friction
Elastic force from a spring
Gravity
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS3-1
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How do non-conservative forces affect mechanical energy?
They always increase mechanical energy.
They have no effect on mechanical energy.
They can either increase or decrease mechanical energy by converting it to or from other forms of energy.
They always decrease mechanical energy.
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the law of conservation of energy based on?
Newton's First Law
The Work-Energy Theorem
The Law of Inertia
The Law of Universal Gravitation
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS3-1
NGSS.HS-PS3-2
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the snowboarder example, what is the initial kinetic energy if the snowboarder starts at 10 m/s and has a mass of 80 kg?
800 J
3200 J
4000 J
1600 J
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS3-1
NGSS.HS-PS3-2
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the final velocity of the snowboarder if the final kinetic energy is 2770 J and the mass is 80 kg?
7.42 m/s
8.32 m/s
9.12 m/s
10.22 m/s
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS3-1
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the sledgehammer example, what is the initial potential energy if the hammer starts at a height of 2.2 meters and has a mass of 5 kg?
107.8 J
98.0 J
112.4 J
120.5 J
Tags
NGSS.HS-PS3-1
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
4th Grade

20 questions
Figurative Language Review
Quiz
•
6th Grade
Discover more resources for Science

33 questions
Grade 6 Quarter 3 PMA 5 Review
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

85 questions
Midpoint D1 Review
Quiz
•
8th Grade

20 questions
Rocks and The Rock Cycle
Quiz
•
6th Grade

12 questions
Ecological Succession
Quiz
•
7th Grade

12 questions
Newton's Laws of Motion
Lesson
•
6th - 8th Grade

10 questions
Exploring the Rock Cycle: Types and Formation
Interactive video
•
6th - 8th Grade

10 questions
Exploring the Layers of the Earth
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Pure Substances & Mixtures
Quiz
•
8th Grade