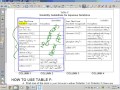
Exploring Solubility Guidelines in Aqueous Solutions
Interactive Video
•
Science
•
6th - 10th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Ethan Morris
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is one of the main characteristics of ionic substances discussed in the introduction?
They are always solid at room temperature.
They form covalent bonds.
They dissolve readily in water.
They do not dissolve in water.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the purpose of using Table F in chemistry?
To calculate the molarity of a solution.
To determine the boiling point of solutions.
To predict whether a precipitate will form.
To measure the pH of a solution.
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following ions always forms soluble compounds with no exceptions?
Sulfate (SO4 2-)
Lead (Pb2+)
Nitrate (NO3-)
Silver (Ag+)
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens when halides are combined with silver, lead, or mercury?
They evaporate.
They form precipitates.
They form soluble compounds.
They form gases.
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the abbreviation for precipitate?
PPT
PIP
PRC
PCT
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following ions is generally insoluble?
Carbonate (CO3 2-)
Acetate (CH3COO-)
Nitrate (NO3-)
Chlorate (ClO3-)
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the exception for chromate (CrO4 2-) in terms of solubility?
It forms soluble compounds with calcium and magnesium.
It is always insoluble.
It is always soluble.
It forms precipitates with calcium and magnesium.
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

6 questions
Cell Transport-- Passive Transport
Interactive video
•
8th Grade

2 questions
Soluble
Interactive video
•
6th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding the Water Cycle
Interactive video
•
4th - 8th Grade

11 questions
Exploring Ionic and Covalent Bonding Concepts
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Determining Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons from the Periodic Table
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Exploring the Four States of Matter
Interactive video
•
6th - 8th Grade

11 questions
Chemical and Physical Properties Assessment
Interactive video
•
6th - 8th Grade

11 questions
DNA Extraction Techniques and Concepts
Interactive video
•
5th - 8th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

7 questions
History of Valentine's Day
Interactive video
•
4th Grade

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

15 questions
Valentine's Day Trivia
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade
Discover more resources for Science

11 questions
Valentines Day
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

25 questions
Valentine's Day Trivia
Quiz
•
8th Grade

20 questions
Cell Organelles and Functions
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

20 questions
Rocks and The Rock Cycle
Quiz
•
6th Grade

8 questions
Newton's Second Law
Lesson
•
6th - 8th Grade

20 questions
Thermal Energy - Heat Transfer
Quiz
•
6th Grade

10 questions
Exploring the Rock Cycle: Types and Formation
Interactive video
•
6th - 8th Grade

10 questions
Carbon Cycle
Lesson
•
6th - 8th Grade