
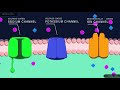
Neuronal Function and Ion Channels
Interactive Video
•
Biology, Science
•
10th - 12th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Easy
Aiden Montgomery
Used 4+ times
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which part of the neuron is responsible for receiving information?
Axon terminal
Cell body
Dendrites
Axon
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the resting membrane potential of a typical neuron?
-55 millivolts
0 millivolts
30 millivolts
-70 millivolts
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What creates the electrochemical gradient across the neuronal membrane?
Electrical impulses
Presence of neurotransmitters
Distribution of ions
Movement of water molecules
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which type of ion channel opens in response to a change in membrane potential?
Ligand-gated ion channels
Mechanically-gated ion channels
Voltage-gated ion channels
Always open ion channels
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary function of the sodium-potassium pump?
To open ion channels
To release neurotransmitters
To transport ions against their concentration gradient
To generate action potentials
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens during depolarization of a neuron?
The membrane potential becomes less negative and more positive
The potassium channels close
The membrane potential becomes more negative
The sodium channels close
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
During which period can a neuron not fire another action potential, no matter the stimulus strength?
Relative refractory period
Absolute refractory period
Resting period
Depolarization period
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

10 questions
China's Economic Growth and Challenges
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Cardiac Anatomy and Function Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Innovative Urban Transportation
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding the Evolution and Future of Computing Technology
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Stress and the Immune System
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Nuclear Explosions and Their Impact
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Jaeger Technology and Engineering Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
Probability Practice
Quiz
•
4th Grade

15 questions
Probability on Number LIne
Quiz
•
4th Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

6 questions
Appropriate Chromebook Usage
Lesson
•
7th Grade

10 questions
Greek Bases tele and phon
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

20 questions
Food Chains and Food Webs
Quiz
•
7th - 12th Grade

65 questions
Review for TEST 1
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Food Webs and Energy Pyramids
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

15 questions
Cell Cycle
Quiz
•
10th Grade

25 questions
Mock STAAR Review 2
Quiz
•
12th Grade

5 questions
Inherited and Acquired Traits of Animals
Interactive video
•
4th Grade - University

48 questions
Unit 8B: Plant System
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

36 questions
DNA & Protein Synthesis 3.1.1-3.1.3
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade