Acid-Base Chemistry and pH Calculations
Interactive Video
•
Chemistry, Science
•
10th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Jackson Turner
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why was the hydrolysis equation for aluminum chloride not written in the previous video?
It is a neutral compound.
It is not relevant to the topic.
It is a very complicated equation.
It is a very simple equation.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following ions is considered neutral?
Iron
Aluminum
Chromium
Chloride
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What characteristic do small, highly charged cations share?
They have no charge.
They are always neutral.
They act as bases.
They act as acids.
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to water molecules when they surround an aluminum ion in a salt solution?
They form a hydration sphere.
They dissociate completely.
They form a crystal structure.
They become neutral.
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
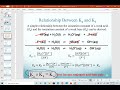
What is the relationship between Ka and Kb for a conjugate acid-base pair?
Ka times Kb equals Kw.
Ka is always greater than Kb.
Ka is always less than Kb.
Ka and Kb are unrelated.
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the value of Kw at 25-degrees Celsius?
1.0 times 10 to the minus 21
1.0 times 10 to the minus 14
1.0 times 10 to the minus 7
1.0 times 10 to the minus 10
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How do you calculate the Kb of an ion if you know the Ka of its conjugate acid?
Subtract Kw from the Ka of the conjugate acid.
Multiply Kw by the Ka of the conjugate acid.
Divide Kw by the Ka of the conjugate acid.
Add Kw to the Ka of the conjugate acid.
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Understanding Salt Solutions
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Solubility and Common Ion Effects
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Calculating pH and Percent Ionization of Weak Acids and Bases
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Acid-Base Reactions and Solutions
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Acid-Base Equilibrium Concepts
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Equilibrium Constant and Water Properties
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
ICE Table and Formula Method Concepts
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Acid-Base Reactions and Concepts
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

12 questions
Unit Zero lesson 2 cafeteria
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Nouns, nouns, nouns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

11 questions
All about me
Quiz
•
Professional Development

20 questions
Lab Safety and Equipment
Quiz
•
8th Grade

13 questions
25-26 Behavior Expectations Matrix
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Digital Citizenship Essentials
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Discover more resources for Chemistry

20 questions
Lab Safety and Lab Equipment
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Lab Equipment Quiz Chemistry
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

19 questions
Lab Safety & Lab Equipment
Quiz
•
10th Grade

30 questions
ACA Unit 1 Atomic Structure
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

21 questions
Lab Safety
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
States of Matter and Phase Changes
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

8 questions
Metric System
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Metric Conversions
Quiz
•
11th Grade