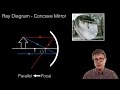
Properties and Functions of Mirrors
Interactive Video
•
Physics, Science
•
10th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Liam Anderson
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary function of a mirror in a telescope?
To refract light
To emit light
To absorb light
To focus light
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How does the angle of incidence compare to the angle of reflection in a mirror?
They are unrelated
The angle of incidence is always greater
The angle of reflection is always greater
They are equal
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which type of mirror creates a virtual image that appears behind the mirror?
Plane mirror
None of the above
Convex mirror
Concave mirror
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In a plane mirror, why does an image appear reversed?
Because the mirror flips the image vertically
Because the mirror distorts the image
Because the mirror flips the image horizontally
Because the mirror rotates the image
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the center of curvature in a concave mirror?
The point where all light rays converge
The center of the sphere from which the mirror is a part
The center of the mirror's surface
The point on the mirror's surface closest to the object
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How does a real image differ from a virtual image in a concave mirror?
A real image can be projected onto a screen
A real image is always upright
A real image is always larger
A real image is always virtual
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the image when an object is placed inside the focal length of a concave mirror?
The image remains unchanged
The image becomes smaller and inverted
The image disappears
The image becomes larger and upright
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

2 questions
Why Am I Upside-Down When I Look in a Spoon?
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

11 questions
Mirror Properties and Image Formation
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

8 questions
Riddle: How does your reflection flip when you bend a spoon inward?
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Concave Mirror Image Formation Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

8 questions
Reflection through Spherical Mirrors
Interactive video
•
KG - University

2 questions
Riddle: How does your reflection flip when you bend a spoon inward?
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Concave and Convex Mirrors Quiz
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

3 questions
Using Light: Summing Up
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Nouns, nouns, nouns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
9/11 Experience and Reflections
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

11 questions
All about me
Quiz
•
Professional Development

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

9 questions
Tips & Tricks
Lesson
•
6th - 8th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

15 questions
Position vs. Time and Velocity vs. Time Graphs
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Using Scalar and Vector Quantities
Quiz
•
8th - 12th Grade

14 questions
Distance & Displacement
Quiz
•
11th Grade

5 questions
Reading Motion Graphs
Lesson
•
8th - 10th Grade

8 questions
Distance Time Graphs
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

13 questions
Velocity Graphs Position vs. Time
Quiz
•
10th - 11th Grade

36 questions
Unit 2 - Waves Review - 2025
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Significant Figures
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade