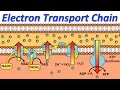
Mitochondrial Function and Processes
Interactive Video
•
Biology, Science
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Sophia Harris
Used 1+ times
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary function of mitochondria in cells?
To transport nutrients
To synthesize proteins
To produce ATP
To store genetic information
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which part of the mitochondria is involved in the electron transport chain?
Outer membrane
Cytoplasm
Inner membrane
Mitochondrial matrix
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the role of the electron transport chain in ATP production?
To synthesize proteins
To transport electrons and create a proton gradient
To store energy
To break down glucose
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which molecule acts as a mobile electron carrier in the electron transport chain?
ATP
NADH
Cytochrome c
FADH2
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following is NOT a component of the electron transport chain?
Complex I
Complex II
Cytochrome c
ATP synthase
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the significance of the proton gradient in mitochondria?
It breaks down proteins
It transports nutrients
It drives ATP synthesis
It stores genetic information
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How do protons move back into the mitochondrial matrix?
Through the cytoplasm
Via ATP synthase
Via electron carriers
Through the outer membrane
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Popular Resources on Wayground

8 questions
2 Step Word Problems
Quiz
•
KG - University

20 questions
Comparing Fractions
Quiz
•
4th Grade

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

10 questions
Latin Bases claus(clois,clos, clud, clus) and ped
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

7 questions
The Story of Books
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

20 questions
Cell Organelles
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Macromolecules
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Cell Organelles
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
DNA & Protein Synthesis
Quiz
•
9th Grade

14 questions
Ecological Succession: Primary and Secondary
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
FAKE IT TILL YOU MAKE IT Organelles
Quiz
•
10th Grade

51 questions
Weather, Climate Change, Cycles
Quiz
•
9th Grade

7 questions
Amoeba Sisters Dihybrid Cross Punnett Square
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade