
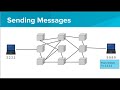
Understanding Internet Routing
Interactive Video
•
Computers
•
7th - 12th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Medium
Mia Campbell
Used 3+ times
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the main limitation of IPv4 that has led to the transition to IPv6?
IPv4 does not support DNS.
IPv4 is not compatible with routers.
IPv4 addresses are too long.
IPv4 has a limited number of unique addresses.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why do we use DNS when browsing the web?
To connect to routers directly.
To encrypt data.
To map domain names to IP addresses.
To increase internet speed.
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary function of a router in a network?
To store data.
To connect to the internet.
To determine the route for data transmission.
To assign IP addresses.
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which factor is NOT considered when a router determines the best path for data?
Speed of the connection.
Trustworthiness of the router.
Distance to the destination.
Cost in terms of money.
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does redundancy in internet routing ensure?
Faster internet speeds.
Lower internet costs.
Single path data transmission.
Reliability and fault tolerance.
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How does having multiple paths between devices benefit the internet?
It decreases data transmission speed.
It improves reliability and fault tolerance.
It makes the system more complex.
It reduces the number of routers needed.
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens if a router in the network fails?
Data is rerouted through alternative paths.
The failed router is immediately replaced.
The entire internet stops working.
All connected devices lose connection.
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
Probability Practice
Quiz
•
4th Grade

15 questions
Probability on Number LIne
Quiz
•
4th Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

6 questions
Appropriate Chromebook Usage
Lesson
•
7th Grade

10 questions
Greek Bases tele and phon
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade
Discover more resources for Computers

10 questions
Exploring Digital Citizenship Essentials
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
![[AP CSP] JavaScript Programming Quiz](https://cf.quizizz.com/image/image-loader.svg)
14 questions
[AP CSP] JavaScript Programming Quiz
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Understanding Computers and Computer Engineering
Interactive video
•
7th - 12th Grade

37 questions
Python - Tuples, Lists, and List Methods
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

60 questions
MOS Word Home, Insert, Reference Ribbon Basics
Quiz
•
9th Grade