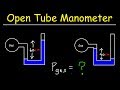
Understanding Open Tube Manometers
Interactive Video
•
Physics, Chemistry, Science
•
10th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Liam Anderson
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary condition for a manometer system to remain in equilibrium?
The density of the fluid must be variable.
The pressure on both sides must be different.
The forces on both sides must be equal.
The fluid must be at a constant temperature.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How is the pressure of a fluid due to its weight calculated?
Density times gravitational acceleration times height
Volume times height
Density times volume
Force times area
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the gauge pressure in a manometer?
The total pressure of the gas
The difference between the gas pressure and atmospheric pressure
The pressure of the atmosphere
The pressure of the fluid at the bottom
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the second problem, what is the relationship between the gas pressure and atmospheric pressure?
Gas pressure is unrelated to atmospheric pressure
Gas pressure is higher than atmospheric pressure
Gas pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure
Gas pressure is lower than atmospheric pressure
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the gauge pressure when the gas pressure is less than atmospheric pressure?
It becomes positive
It becomes zero
It becomes negative
It remains unchanged
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How can you determine if the gauge pressure is positive or negative?
By measuring the height of the fluid column
By comparing the gas pressure to the atmospheric pressure
By comparing the gas pressure to the fluid pressure
By calculating the fluid's density
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the gauge pressure if the gas pressure is 70,000 pascals and atmospheric pressure is 100,000 pascals?
30,000 pascals
70,000 pascals
-30,000 pascals
100,000 pascals
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Natural Convection Concepts and Principles
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

8 questions
Hidrostática
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

4 questions
Understanding Pressure Due to Fluids: Deriving Equations and Solving Examples
Interactive video
•
10th Grade - University

11 questions
Understanding U-Shaped Tube Problems
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Forces in Fluids: Video Assessment
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Fluid Dynamics and Energy Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

8 questions
El principio de Arquímedes o 🚢 ¿Por qué flotan los barcos?
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Fluid Pressure and Effective Stress
Interactive video
•
10th Grade - University
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Video Games
Quiz
•
6th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

10 questions
UPDATED FOREST Kindness 9-22
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

20 questions
US Constitution Quiz
Quiz
•
11th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Digital Citizenship Essentials
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

20 questions
Claim Evidence Reasoning
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

14 questions
Distance & Displacement
Quiz
•
11th Grade

17 questions
Free Body Diagrams
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Motion Graphs
Quiz
•
11th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Distance & Displacement
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

19 questions
Graphing Motion Review
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Multiplying/ Dividing Significant Figures
Quiz
•
11th Grade

23 questions
Unit 1 Graphing and Pendulum
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade