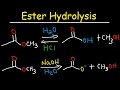
Acid and Base Catalysis Concepts
Interactive Video
•
Chemistry, Science
•
10th Grade - University
•
Hard
Ethan Morris
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What are the products when methyl acetate reacts with water and HCl under acidic conditions?
Carboxylic acid and methanol
Acetic acid and ethanol
Ethanol and acetic acid
Methanol and ethyl acetate
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the acid-catalyzed ester hydrolysis, which ion is formed when HCl is added to water?
Na+
H3O+
Cl-
OH-
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
During the acid-catalyzed mechanism, which oxygen in the ester is more likely to be protonated?
The oxygen with no charge
The oxygen with a negative formal charge
The oxygen bonded to carbon
The oxygen with a positive formal charge
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the role of water in the acid-catalyzed ester hydrolysis mechanism?
Acts as a weak base
Acts as a strong acid
Acts as a nucleophile
Acts as a catalyst
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the final product of the acid-catalyzed ester hydrolysis?
Ester
Methanol
Deprotonated carboxylic acid
Protonated carboxylic acid
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the base-catalyzed mechanism, what is the role of hydroxide?
Acts as a catalyst
Acts as an acid
Acts as a solvent
Acts as a nucleophile
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to methoxide in the base-catalyzed ester hydrolysis?
It acts as a nucleophile
It forms a double bond
It attacks the carbonyl carbon
It deprotonates the carboxylic acid
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Acid-Base Reactions and pH
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Alkene - Addition Reactions - Crash Course Organic Chemistry
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

11 questions
Organic Synthesis with Ethers and Epoxides Quiz
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

2 questions
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives & Hydrolysis Reactions: Crash Course Organic Chemistry
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

8 questions
Fischer Esterification and Saponification
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

8 questions
Hydrohalogenation, Hydration, Dihalogenation
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

11 questions
Alpha Halogenation and Related Reactions Quiz
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

8 questions
Organic Chemistry Synthesis Challenge 4
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Video Games
Quiz
•
6th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

10 questions
UPDATED FOREST Kindness 9-22
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

20 questions
US Constitution Quiz
Quiz
•
11th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Digital Citizenship Essentials
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Discover more resources for Chemistry

15 questions
Isotopes/structure of an atom
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Metric Conversions
Quiz
•
11th Grade

20 questions
Atomic Structure
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

20 questions
COUNTING ATOMS
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Periodic Trends
Quiz
•
10th Grade

15 questions
Exploring the Unique Properties of Water
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

17 questions
CHemistry Unit 7 Dimensional Analysis Practice
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

47 questions
Unit #4 Electron KAP Test Review
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade