
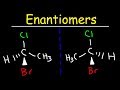
Understanding Enantiomers
Interactive Video
•
Chemistry, Science
•
10th - 12th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Ethan Morris
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What are enantiomers?
Molecules with different chemical formulas
Superimposable mirror images
Non-superimposable mirror images
Identical molecules
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How can you draw the enantiomer of a molecule with one chiral center?
By rotating the molecule 90 degrees
By drawing its mirror image
By adding more atoms
By changing its chemical formula
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which atom has the highest priority when assigning configurations?
Methyl group
Chlorine
Bromine
Hydrogen
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What configuration does a clockwise rotation indicate when the lowest priority group is in the back?
R configuration
S configuration
T configuration
U configuration
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What should you do to draw the enantiomer of a molecule with two chiral centers?
Rotate the molecule 180 degrees
Reverse the configuration of both chiral centers
Add a line of symmetry
Change the chemical formula
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is a meso compound?
A compound with different chemical formulas
A compound with identical configurations
A compound with a line of symmetry
A compound with no chiral centers
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In a Fischer projection, what happens when you reverse the positions of hydrogen and fluorine?
The molecule becomes superimposable
The molecule's formula changes
The molecule becomes a meso compound
The enantiomer is drawn
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Understanding Fischer Projections and Chirality
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

7 questions
Exploring Black Holes in the Universe
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Fischer Projections and Stereochemistry
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Patrick Gallagher Keynote, NIST Cloud Computing Forum and Workshop IV
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

8 questions
Periodic Table Part 3: Alkaline Earth Metals (Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra)
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

6 questions
3 Animals That Breathe Through Their Butts
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

6 questions
Sustainable green towers constructed in central Taiwan
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

11 questions
Newman and Fischer Projections Quiz
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

29 questions
Alg. 1 Section 5.1 Coordinate Plane
Quiz
•
9th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

11 questions
FOREST Effective communication
Lesson
•
KG

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade
Discover more resources for Chemistry

22 questions
Unit 9 Gas Law Quiz
Quiz
•
10th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Types of Chemical Reactions
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Types of Chemical Reactions
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Acids and Bases
Quiz
•
10th Grade

7 questions
GCSE Chemistry - Balancing Chemical Equations #4
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Chemistry: Classification of Matter
Quiz
•
10th Grade

40 questions
Unit 3 (Part 1) Chemical Equations & Reactions Review Game
Quiz
•
8th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Stoichiometry Review
Quiz
•
10th Grade