Understanding Heating and Cooling Curves of Water
Interactive Video
•
Physics, Chemistry, Science
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Medium
Amelia Wright
Used 9+ times
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
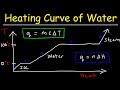
What happens to the temperature of ice as it is heated from -20°C to 0°C?
It decreases.
It increases.
It remains constant.
It fluctuates.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
During the phase change from ice to liquid water, what type of energy increases?
Thermal energy
Potential energy
Mechanical energy
Kinetic energy
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the enthalpy of vaporization for water?
4.18 kJ/mol
40.7 kJ/mol
6 kJ/mol
2 kJ/mol
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How does the specific heat capacity of water affect the slope of its heating curve?
Higher specific heat capacity results in a steeper slope.
The slope is always constant regardless of specific heat capacity.
Lower specific heat capacity results in a steeper slope.
Specific heat capacity does not affect the slope.
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why does steam have a steeper slope on the heating curve compared to liquid water?
Steam absorbs more heat energy.
Steam has a higher specific heat capacity.
Steam releases more heat energy.
Steam has a lower specific heat capacity.
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What type of process is the cooling curve of water?
Endothermic
Exothermic
Isothermal
Adiabatic
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
During the cooling curve, what happens to the potential energy of steam as it condenses?
It remains constant.
It decreases.
It fluctuates.
It increases.
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy
Already have an account?
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Honoring the Significance of Veterans Day
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

9 questions
FOREST Community of Caring
Lesson
•
1st - 5th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Veterans Day: Facts and Celebrations for Kids
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

19 questions
Veterans Day
Quiz
•
5th Grade

14 questions
General Technology Use Quiz
Quiz
•
8th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

15 questions
Circuits, Light Energy, and Forces
Quiz
•
5th Grade

19 questions
Thanksgiving Trivia
Quiz
•
6th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

10 questions
Types of Chemical Reactions
Quiz
•
10th Grade

14 questions
Bill Nye Waves
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

14 questions
Work, Energy and Power
Lesson
•
10th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Exploring the Phenomenon of Static Electricity
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Exit Check 7.2: Electromagnetic Waves
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Exit Check 7.3 - Analog and Digital
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Newton's Third Law
Quiz
•
7th - 11th Grade

9 questions
Exit Check 7.4 - Wave Particle Duality
Quiz
•
9th Grade