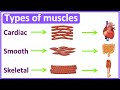
Muscle Types and Functions in the Human Body
Interactive Video
•
Biology, Science, Physical Ed
•
6th - 7th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
6 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary function of muscles in the human body?
To provide structural support
To produce hormones
To store energy
To facilitate movement and other functions
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which type of muscle is found in the heart?
Smooth muscle
Skeletal muscle
Cardiac muscle
Voluntary muscle
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How do smooth muscles function in the body?
They contract and relax voluntarily
They are responsible for conscious movements
They operate involuntarily to aid digestion and blood flow
They are attached to bones
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is a characteristic feature of cardiac muscles?
They are long and tubular
They have multiple nuclei per fiber
They are spindle-shaped
They are short, branched, and striated
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Where are skeletal muscles typically found?
In the heart
In hollow organs
Attached to bones
In blood vessels
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What distinguishes skeletal muscles from other muscle types?
They are spindle-shaped
They have a single nucleus per fiber
They are responsible for voluntary movements
They are involuntary
Similar Resources on Wayground

6 questions
Muscular System
Interactive video
•
7th Grade

6 questions
Understanding Muscle Growth
Interactive video
•
5th - 6th Grade

10 questions
Muscle Mechanics and Movement in the Human Body
Interactive video
•
6th - 8th Grade

11 questions
Exploring the Musculoskeletal System for 7th Grade Science
Interactive video
•
6th - 8th Grade

11 questions
Muscular System Concepts and Functions
Interactive video
•
5th - 6th Grade

11 questions
Exploring The Major Human Body Systems And Their Functions
Interactive video
•
6th - 8th Grade

3 questions
I WONDER - Are Jellyfish Actually Fish?
Interactive video
•
KG - 6th Grade

11 questions
Human Body Systems and Functions
Interactive video
•
6th - 8th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Nouns, nouns, nouns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
Appointment Passes Review
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

11 questions
All about me
Quiz
•
Professional Development

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

20 questions
Grammar Review
Quiz
•
6th - 9th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

23 questions
Lab Equiptment/ Lab Safety
Quiz
•
7th Grade

20 questions
Cell Structures
Quiz
•
7th Grade

18 questions
Cell theory & Scientists
Quiz
•
7th Grade

20 questions
Levels of Organization in Living Things
Quiz
•
7th Grade

15 questions
Characteristics of Life
Quiz
•
7th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Fabulous Food Chains
Quiz
•
4th - 8th Grade

12 questions
cell transport day 2 warm up
Quiz
•
7th - 9th Grade

38 questions
Cells & Viruses 25-26
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade