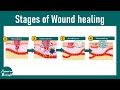
The Stages of Wound Healing Explained
Interactive Video
•
Biology, Science, Other
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which type of tissue is known for its high regenerative potential?
Muscle tissue
Connective tissue
Bone tissue
Nerve tissue
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary goal of the hemostasis phase in wound healing?
To initiate immune response
To prevent blood loss
To promote tissue growth
To remove dead cells
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which cells are first to respond to a wound during the inflammatory phase?
Neutrophils
Macrophages
Fibroblasts
Keratinocytes
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What role do macrophages play in the inflammatory phase?
They secrete growth factors for angiogenesis
They produce collagen
They form blood clots
They migrate to close the wound
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which factor is secreted by fibroblasts to aid in tissue remodeling?
Fibroblast growth factor
PDGF
VEGF
TGF-beta
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
During the proliferation phase, what process is responsible for supplying oxygen to the wound site?
Vasoconstriction
Re-epithelialization
Angiogenesis
Fibrosis
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the main function of re-epithelialization in wound healing?
To close the wound with new epithelial cells
To form a blood clot
To remodel the extracellular matrix
To secrete cytokines
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

8 questions
CLEAN : Trickle of British tourists dashes Cyprus tourism hopes
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Distance Learning and Educational Practices
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
The Philosophy of Banksy
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Subtracting Polynomials Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
Geography and Cultural Insights Assessment
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Theatrical Release Dynamics and Strategies
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Functions of the Immune System
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

20 questions
Brand Labels
Quiz
•
5th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Ice Breaker Trivia: Food from Around the World
Quiz
•
3rd - 12th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
ELA Advisory Review
Quiz
•
7th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

10 questions
Multiplication and Division Unknowns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
Exploring Digital Citizenship Essentials
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

20 questions
Cell Organelles
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Cell Transport
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Cell organelles and functions
Quiz
•
10th Grade

22 questions
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Cell Organelles
Quiz
•
9th Grade

25 questions
photosynthesis and cellular respiration
Quiz
•
9th Grade

16 questions
AP Biology: Unit 1 Review (CED)
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Biomolecules
Quiz
•
9th Grade