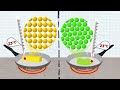
Molecular Movement and Phase Changes in Butter and Olive Oil
Interactive Video
•
Physics, Chemistry, Science
•
6th - 8th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
7 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the state of butter at room temperature?
Liquid
Gas
Solid
Plasma
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does temperature measure in a substance?
The average kinetic energy of molecules
The color of the substance
The volume of the substance
The weight of the substance
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why do butter and olive oil have different phases at the same temperature?
Because they have different colors
Because their molecules move differently
Because they have different average kinetic energies
Because they have different weights
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the molecules in butter when energy is added?
They change color
They become heavier
They move more freely
They stop moving
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
At what point does butter start to melt?
When it is mixed with oil
When it is cooled
When it loses energy
When it gains enough energy
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What determines the phase of a substance at a given temperature?
The substance's volume
The temperature and the substance itself
The substance's weight
The substance's color
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Can two substances be in the same phase at the same temperature?
Yes, always
Only if they are mixed
No, never
Yes, it depends on the substances
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Kinetic Energy and Phase Changes
Interactive video
•
6th - 8th Grade

11 questions
The Fascinating World of Phase Changes in Matter
Interactive video
•
6th - 8th Grade

10 questions
Physical and Chemical Changes Assessment
Interactive video
•
6th - 7th Grade

6 questions
Volátil
Interactive video
•
4th - 9th Grade

11 questions
Energy and Sound Concepts Assessment
Interactive video
•
6th - 8th Grade

11 questions
Energy Transfer and Heat Concepts
Interactive video
•
7th - 8th Grade

6 questions
Ice Pop Modeling Tool Concepts
Interactive video
•
6th - 8th Grade

6 questions
Freezing
Interactive video
•
6th - 9th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Nouns, nouns, nouns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
Appointment Passes Review
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

11 questions
All about me
Quiz
•
Professional Development

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

20 questions
Grammar Review
Quiz
•
6th - 9th Grade