
Wind and Weathering Processes
Interactive Video
•
Science, Geography, Other
•
4th - 5th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What are the three processes that shape the Earth discussed in the lesson?
Weathering, erosion, and deposition
Volcanism, tectonics, and sedimentation
Erosion, sedimentation, and volcanism
Weathering, tectonics, and erosion
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How does wind contribute to the weathering of rocks?
By heating the rocks
By picking up and slamming sediment against them
By freezing and thawing
By dissolving them in water
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the role of wind in erosion?
It carries sediment to new locations
It melts the rocks
It compresses the rocks
It dissolves the rocks
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What conditions are necessary for sand dunes to form?
Volcanic activity
Cold temperatures and ice
High humidity and rain
Steady winds and abundant sand
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How do obstacles like rocks and plants affect sand movement?
They speed up the sand
They block and trap sand, forming dunes
They dissolve the sand
They heat the sand
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
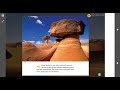
What are toadstool cap rocks?
Rocks shaped by tectonic movements
Rocks shaped by differential weathering
Rocks formed by sediment deposition
Rocks formed by volcanic activity
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why is the bottom of a toadstool cap rock more weathered than the top?
The top is constantly submerged in water
The top is made of harder material
The bottom is softer and more exposed to wind
The bottom is protected by vegetation
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

6 questions
I WONDER - What Is A Landfill?
Interactive video
•
KG - 6th Grade

6 questions
I WONDER - Was The Stegosaurus A Herbivore?
Interactive video
•
KG - 6th Grade

6 questions
Where Do Icicles Come From?
Interactive video
•
1st - 6th Grade

6 questions
Why Sea Cows Are Awesome? Animal Science for Kids
Interactive video
•
1st - 6th Grade

6 questions
Habitats – What's that noise?
Interactive video
•
1st - 6th Grade

6 questions
SYND 5-5-74 D'ESTAING VOTES
Interactive video
•
6th - 7th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

7 questions
History of Valentine's Day
Interactive video
•
4th Grade

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

15 questions
Valentine's Day Trivia
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade
Discover more resources for Science

20 questions
Weathering, Erosion, Deposition
Quiz
•
5th Grade

15 questions
Physical and Chemical Changes
Quiz
•
4th Grade

28 questions
4th Grade The Need for Speed
Quiz
•
3rd - 5th Grade

20 questions
Food Chains and Food Webs Review
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
The Water Cycle
Quiz
•
4th - 5th Grade

21 questions
Solar System Review
Quiz
•
5th Grade

10 questions
Food chains and food webs
Interactive video
•
4th Grade

20 questions
Food Webs
Quiz
•
5th Grade