
Understanding Series and Parallel Circuits
Interactive Video
•
Physics, Mathematics, Science
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary focus when comparing series and parallel circuits?
The type of resistors used
The size of the resistors
The arrangement of resistors and application of voltage
The color of the wires
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
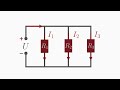
In a series circuit, how are the resistors connected?
In a star pattern
In a chain
In a loop
In a grid
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How is the total current in a parallel circuit determined?
By dividing the total voltage by the total resistance
By adding the individual currents
By subtracting the smallest current from the largest
By multiplying the individual currents
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In a series circuit, how does the current through each resistor compare?
It is different for each resistor
It is half the total current
It is zero
It is the same through all resistors
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is true about the voltage across resistors in a parallel circuit?
It is double the source voltage
It is zero
It varies for each resistor
It is the same across all resistors
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the total voltage in a series circuit?
It is the same as the voltage across the first resistor
It is zero
It is the sum of the individual voltages across each resistor
It is double the source voltage
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How is the total resistance in a series circuit calculated?
By adding the resistances
By taking the reciprocal of the sum of reciprocals
By multiplying the resistances
By subtracting the smallest resistance from the largest
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Popular Resources on Wayground

8 questions
Spartan Way - Classroom Responsible
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

14 questions
Boundaries & Healthy Relationships
Lesson
•
6th - 8th Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

3 questions
Integrity and Your Health
Lesson
•
6th - 8th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

9 questions
FOREST Perception
Lesson
•
KG

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

10 questions
Exit Check 4.5 - Impulse
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Simple Machines and Mechanical Advantage Quiz
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Electricity/Magnets
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Light Vs. Sound Waves
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

14 questions
Bill Nye Waves
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

37 questions
CIA #3 Study Guide: ACPS
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Waves
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Exploring the Properties of Waves
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade