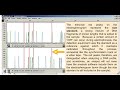
Electropherogram Analysis Concepts
Interactive Video
•
Biology, Science, Chemistry
•
10th - 12th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What do the numbers along the y-axis of an electropherogram represent?
Peak height
Relative fluorescent units
DNA fragment length
Allele frequency
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How is a male's gender indicated on an electropherogram?
A single red peak
Two peaks: one x-allele and one y-allele
A single tall green peak
Multiple blue peaks
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the purpose of using different colored dyes in electropherograms?
To enhance the fluorescence
To reduce baseline noise
To increase the peak height
To distinguish alleles of similar length
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What do the extra tall red peaks on an electropherogram represent?
Allele frequency
Homozygous genotype
Size standard
Baseline noise
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why are red peaks disregarded during DNA profile analysis?
They show the gender of the subject
They are used for calibration and not for analysis
They indicate a heterozygous genotype
They represent baseline noise
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does a single peak at a locus indicate?
Heterozygous genotype
Baseline noise
Stutter
Homozygous genotype
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why are homozygous peaks generally taller than heterozygous peaks?
They contain more genetic material
They are amplified by different dyes
They are closer to the baseline
They are measured in RFUs
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

6 questions
Properties of Waves and Calculating Wave Speed
Interactive video
•
10th Grade - University

6 questions
Sharks: Diversity, Threats, and Conservation Efforts
Interactive video
•
KG - University

6 questions
Mount Everest: From Triumph to Trash
Interactive video
•
KG - University

11 questions
Alpine Climbing Challenges and Strategies
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

6 questions
How to determine if the discontinuities are holes or asymptotes
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

6 questions
Fundamentals of Genetics: Video Quiz
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Cybersecurity Framework Overview Michael Daniel
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

8 questions
CLEAN : In northern Sweden, climate change reshapes Arctic landscapes
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

8 questions
2 Step Word Problems
Quiz
•
KG - University

20 questions
Comparing Fractions
Quiz
•
4th Grade

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

10 questions
Latin Bases claus(clois,clos, clud, clus) and ped
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

7 questions
The Story of Books
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

20 questions
Cell Organelles
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Macromolecules
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
FAKE IT TILL YOU MAKE IT Organelles
Quiz
•
10th Grade

7 questions
Amoeba Sisters Dihybrid Cross Punnett Square
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

17 questions
FAKE IT TILL YOU MAKE IT Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
Quiz
•
10th Grade

10 questions
Sex-Linked Traits
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

32 questions
Evidence of Evolution - U7 Review
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Ameoba Sisters: Introduction to cells
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade