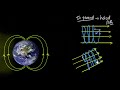
Charged Particles in Magnetic Fields
Interactive Video
•
Physics, Science, Other
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary reason auroras are typically observed at the poles?
The atmosphere is thinner at the poles.
The poles are closer to the sun.
The magnetic field lines converge at the poles.
The poles have a higher concentration of charged particles.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which equation is used to calculate the force on a charged particle in a magnetic field?
Lorentz Force Equation
Newton's Second Law
Ohm's Law
Coulomb's Law
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
When a charged particle moves perpendicular to a magnetic field, what path does it follow?
A zigzag path
A circular path
A parabolic path
A straight line
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What tool is used to determine the direction of the force on a charged particle in a magnetic field?
Left-hand rule
Vector addition
Right-hand rule
Magnetic compass
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the speed of a charged particle moving in a magnetic field?
It decreases
It fluctuates
It increases
It remains constant
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How does a charged particle move when its velocity is not perpendicular to the magnetic field?
In a random path
In a straight line
In a zigzag pattern
In a helical path
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the effect of a magnetic field on a charged particle moving parallel to it?
It changes the particle's charge
It accelerates the particle
It has no effect on the particle
It decelerates the particle
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Magnetic Fields and Charged Particles
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Charged Particles in Magnetic Fields
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Uniform Electric Fields
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Particle Accelerators
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Magnetic and Electric Forces Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Magnetic Forces on Charged Particles
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Electric Potential and Electric Potential Energy
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Magnetic Forces and Fields Concepts
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

50 questions
Trivia 7/25
Quiz
•
12th Grade

11 questions
Standard Response Protocol
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

11 questions
Negative Exponents
Quiz
•
7th - 8th Grade

12 questions
Exponent Expressions
Quiz
•
6th Grade

4 questions
Exit Ticket 7/29
Quiz
•
8th Grade

20 questions
Subject-Verb Agreement
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
One Step Equations All Operations
Quiz
•
6th - 7th Grade

18 questions
"A Quilt of a Country"
Quiz
•
9th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

50 questions
Trivia 7/25
Quiz
•
12th Grade

20 questions
Subject-Verb Agreement
Quiz
•
9th Grade

18 questions
"A Quilt of a Country"
Quiz
•
9th Grade

6 questions
RL.10.1 Cite Evidence
Quiz
•
10th Grade

10 questions
Characteristics of Life
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

14 questions
Algebra 1 SOL Review #1
Quiz
•
9th Grade