Kepler's Laws and Orbital Motion
Interactive Video
•
Physics, Mathematics, Science
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
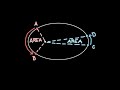
What does Kepler's Second Law state about the motion of an object in orbit?
It maintains a constant speed.
It sweeps through equal areas in equal times.
It moves faster at aphelion.
It moves in a perfect circle.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
If an object takes the same time to travel from point A to B and from C to D, what can be said about the areas covered?
The area from A to B is larger.
The area from C to D is larger.
Both areas are equal.
The areas cannot be compared.
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
At which point in its orbit does Earth travel faster?
At aphelion.
At perihelion.
It travels at a constant speed.
At the midpoint.
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is Earth's average velocity in its orbit?
29.3 km/s
30 km/s
28 km/s
29.8 km/s
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How is the length of an arc in an elliptical orbit calculated?
By multiplying the radius by the angle.
By dividing the radius by the angle.
By adding the radius and the angle.
By subtracting the angle from the radius.
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does the term 'dA/dt' represent in the context of Kepler's Second Law?
The change in area over time.
The change in distance over time.
The change in velocity over time.
The change in mass over time.
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What remains constant according to Kepler's Second Law?
Angular momentum.
Mass of the object.
Change in area over time.
Distance from the focus.
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Rotational Dynamics and Energy Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Angular Momentum and Energy Conservation Quiz
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Angular Momentum and Planetary Motion
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Quantum Numbers and Electron Configurations
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Angular Motion and Kinematics Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Rolling Motion and Energy Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

8 questions
Angular Momentum
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Angular Momentum
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Video Games
Quiz
•
6th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

10 questions
UPDATED FOREST Kindness 9-22
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

20 questions
US Constitution Quiz
Quiz
•
11th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Digital Citizenship Essentials
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

20 questions
Position vs. Time Graphs
Quiz
•
9th Grade

25 questions
Newton's Laws of Motion
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Claim Evidence Reasoning
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

14 questions
Distance & Displacement
Quiz
•
11th Grade

17 questions
Free Body Diagrams
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Exit Check 3.3 - Universal Gravitation
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Motion Graphs
Quiz
•
11th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Exit Check 3.4 - Moon's Orbit
Quiz
•
9th Grade