Electric Field Concepts and Calculations
Interactive Video
•
Physics, Science, Mathematics
•
11th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the main difference between surface charge density and linear charge density?
Linear charge density is measured in micro coulombs per cubic meter.
Surface charge density is measured in micro coulombs per meter.
Linear charge density is measured in micro coulombs per square meter.
Surface charge density is measured in micro coulombs per square meter.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Where is the electric field present in a charged conductor?
Outside the conductor only
Inside the conductor only
Both inside and outside the conductor
Neither inside nor outside the conductor
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
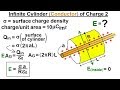
What must be considered when calculating the electric field at a distance from a charged cylinder?
Only the surface charge density
Only the distance from the surface
Both the radius of the cylinder and the distance from the surface
Only the length of the cylinder
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the purpose of the Gaussian surface in this context?
To determine the radius of the cylinder
To enclose the charge and help apply Gauss's Law
To measure the length of the cylinder
To calculate the surface charge density
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the formula for the charge inside the Gaussian surface?
Sigma times the radius of the cylinder
Sigma times the circumference times the length
Sigma times the surface area of the ends
Sigma times the length of the cylinder
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why are the ends of the cylinder not considered in the charge calculation?
Because they are not part of the Gaussian surface
Because they are too small
Because they have no charge
Because they are not conductive
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the terms 'L' and '2π' in the electric field equation derivation?
They are divided by the radius
They are added together
They are multiplied by epsilon
They cancel out
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Understanding the Divergence Theorem and Flux Integrals
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

11 questions
Conductors in Electrostatic Equilibrium - Review for AP Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

11 questions
Electric Field and Charge Calculations
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

6 questions
How to find the surface area of a cylinder
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

8 questions
Surface Area of a Sphere
Interactive video
•
10th Grade - University

11 questions
Surface Area of a Plane Inside a Cylinder
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

11 questions
Surface Area of a Plane Inside a Cylinder
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

8 questions
Optimization 1
Interactive video
•
12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Video Games
Quiz
•
6th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

10 questions
UPDATED FOREST Kindness 9-22
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

20 questions
US Constitution Quiz
Quiz
•
11th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Digital Citizenship Essentials
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

20 questions
Claim Evidence Reasoning
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

14 questions
Distance & Displacement
Quiz
•
11th Grade

17 questions
Free Body Diagrams
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Motion Graphs
Quiz
•
11th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Distance & Displacement
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

19 questions
Graphing Motion Review
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Multiplying/ Dividing Significant Figures
Quiz
•
11th Grade

23 questions
Unit 1 Graphing and Pendulum
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade