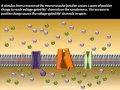
Skeletal Muscle Cell Physiology
Interactive Video
•
Biology, Science, Chemistry
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
9 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary function of the sarcolemma in skeletal muscle cells?
To transport oxygen
To generate ATP
To separate extracellular and intracellular spaces
To store calcium ions
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Where are sodium ions highly concentrated in a resting muscle cell?
In the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Outside the cell
Inside the cell
In the mitochondria
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following is NOT embedded in the sarcolemma?
Voltage-gated sodium channels
Voltage-gated potassium channels
Sodium-potassium ATPase pumps
Calcium ion channels
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What triggers the opening of voltage-gated sodium channels during an action potential?
The release of calcium ions
A decrease in potassium concentration
A wave of positive charge
The binding of ATP
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the term for the process when the inside of the sarcolemma becomes more positively charged?
Hyperpolarization
Repolarization
Polarization
Depolarization
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
When do voltage-gated potassium channels open during an action potential?
When ATP is depleted
When the membrane is at its maximum positive charge
When sodium channels close
When calcium levels increase
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the process called when the membrane potential returns to resting levels?
Hyperpolarization
Equilibrium
Repolarization
Depolarization
8.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which ion flows out of the muscle cell during repolarization?
Chloride
Potassium
Calcium
Sodium
9.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What energy source does the sodium-potassium pump use to restore ion gradients?
Glucose
GTP
ATP
NADH
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Honoring the Significance of Veterans Day
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

9 questions
FOREST Community of Caring
Lesson
•
1st - 5th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Veterans Day: Facts and Celebrations for Kids
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

19 questions
Veterans Day
Quiz
•
5th Grade

14 questions
General Technology Use Quiz
Quiz
•
8th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

15 questions
Circuits, Light Energy, and Forces
Quiz
•
5th Grade

19 questions
Thanksgiving Trivia
Quiz
•
6th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

15 questions
Meiosis vs mitosis
Quiz
•
9th Grade

25 questions
photosynthesis and cellular respiration
Quiz
•
9th Grade

15 questions
DNA Mutations
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Cell Organelles
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Food Chains and Food Webs
Quiz
•
7th - 12th Grade

15 questions
DNA Structure and Replication
Quiz
•
9th Grade

22 questions
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
Quiz
•
9th Grade

21 questions
Cell Cycle and mitosis
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade