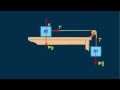
Tension and Acceleration in Two-Block Systems
Interactive Video
•
Physics, Science, Mathematics
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to an object when the sum of all forces acting on it is zero?
It accelerates.
It remains stationary.
It moves at a constant velocity.
It changes direction.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the sample problem, what is the role of the tension in the string?
It prevents the blocks from moving.
It accelerates the sliding block to the right.
It cancels out the gravitational force.
It increases the mass of the blocks.
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How do internal forces affect the motion of the two-block system?
They decrease the system's acceleration.
They have no effect on the system's motion.
They increase the system's acceleration.
They change the direction of the system's motion.
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the acceleration of the two-block system in the sample problem?
Zero.
Twice the gravitational acceleration, 2g.
Half of the gravitational acceleration, g/2.
Equal to gravitational acceleration, g.
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the effect of internal forces on the two-block system?
They cancel each other out.
They increase the system's mass.
They increase the system's speed.
They change the direction of motion.
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the tension in the string when the blocks are accelerating?
Zero.
Equal to the weight of one block, mg.
Half the weight of one block, mg/2.
Twice the weight of one block, 2mg.
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the string tension if the sliding block is held stationary?
It doubles.
It becomes negative.
It equals the weight of one block, mg.
It becomes zero.
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Projectile Motion Formulas
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Forces and Friction in Mechanics
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Spring Dynamics and Energy Calculations
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Work, Energy, and Kinematics Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Forces and Friction in Physics
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Momentum and Impulse in Motion Dynamics
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Gravity and Gravitational Fields
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Oscillation and Spring Dynamics
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Nouns, nouns, nouns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
9/11 Experience and Reflections
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

11 questions
All about me
Quiz
•
Professional Development

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

9 questions
Tips & Tricks
Lesson
•
6th - 8th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

20 questions
Position vs. Time Graphs
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Calculating Net Force
Quiz
•
6th - 9th Grade

15 questions
Position vs. Time and Velocity vs. Time Graphs
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Using Scalar and Vector Quantities
Quiz
•
8th - 12th Grade

14 questions
Distance & Displacement
Quiz
•
11th Grade

20 questions
Acceleration
Quiz
•
9th Grade

5 questions
Reading Motion Graphs
Lesson
•
8th - 10th Grade

8 questions
Distance Time Graphs
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade