
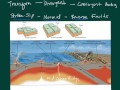
Mechanical Advantage and Rock Cycle Concepts
Interactive Video
•
Science, Physics, Geography
•
6th - 8th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to an oceanic plate when it is subducted under a continental plate?
It remains unchanged.
It rises to the surface and forms mountains.
It melts and contributes to the formation of magma.
It cools down and forms new land.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which type of rock is formed through the process of compaction and cementation of sediments?
Metamorphic rock
Volcanic rock
Igneous rock
Sedimentary rock
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the crayon rock cycle analogy, what does the grinding of crayons represent?
Melting of magma
Formation of igneous rock
Creation of sediments
Weathering of rocks
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the result of applying heat and pressure to the crayon sediments in the analogy?
They remain unchanged.
They form metamorphic rock.
They become a homogeneous mixture.
They turn into igneous rock.
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What type of plate boundary is associated with seafloor spreading?
Transform boundary
Divergent boundary
Convergent boundary
Subduction zone
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How are the Hawaiian Islands formed according to the video?
By erosion of continental crust
Through sediment deposition
By volcanic activity over a hot spot
Through the collision of tectonic plates
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the formula for calculating speed?
Speed = Distance x Time
Speed = Time x Distance
Speed = Distance / Time
Speed = Time / Distance
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Popular Resources on Wayground

8 questions
Spartan Way - Classroom Responsible
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

14 questions
Boundaries & Healthy Relationships
Lesson
•
6th - 8th Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

3 questions
Integrity and Your Health
Lesson
•
6th - 8th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

9 questions
FOREST Perception
Lesson
•
KG

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade
Discover more resources for Science

22 questions
Phases of the moon
Quiz
•
8th Grade

20 questions
Rocks and The Rock Cycle
Quiz
•
6th Grade

20 questions
Flow of Energy
Quiz
•
7th Grade

20 questions
Waves and Wave Properties
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

8 questions
Amoeba Sister Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction
Interactive video
•
8th Grade

10 questions
Exploring the Rock Cycle: Types and Formation
Interactive video
•
6th - 8th Grade

16 questions
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Review
Quiz
•
7th Grade

20 questions
8th Grade Science STAAR Review
Quiz
•
8th Grade