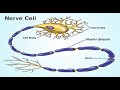
Myelin and Nervous System Functions
Interactive Video
•
Biology, Science, Other
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
9 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary function of myelin in the nervous system?
To act as an electrical insulator
To provide nutrients to neurons
To connect neurons together
To store neurotransmitters
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What are the gaps in the myelin sheath called?
Synaptic clefts
Axon terminals
Dendritic spines
Nodes of Ranvier
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the central nervous system, from which cells is myelin derived?
Neurons
Astrocytes
Glial cells
Schwann cells
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which cells are responsible for creating myelin in the peripheral nervous system?
Ependymal cells
Oligodendrocytes
Microglia
Schwann cells
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the term for axons that are wrapped in myelin?
Non-myelinated fibers
Dendritic fibers
Gray matter
Myelinated fibers
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the collective name for myelinated fibers in the central nervous system?
Neural matter
White matter
Axonal matter
Gray matter
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the appearance of non-myelinated fibers in the central nervous system?
Blue
Red
Gray
White
8.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following is NOT a function of myelin?
Covering axons completely
Providing structural support
Acting as an electrical insulator
Increasing conduction speed
9.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the main difference between myelinated and non-myelinated fibers?
Myelinated fibers are faster in conduction
Non-myelinated fibers are white
Myelinated fibers are found only in the PNS
Non-myelinated fibers are covered by myelin
Similar Resources on Wayground

9 questions
Telophase 1 and Anaphase 1 Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Brain Structure and Function Assessment
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

7 questions
Nervous System - Amoeba Sisters
Interactive video
•
9th Grade

11 questions
Peripheral Nervous System Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Peripheral Nervous System Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

6 questions
CLEAN : Togo court confirms Gnassingbes presidential poll win
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Nervous System and Neonicotinoids
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Neural Signaling and Impulse Transmission
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

18 questions
Writing Launch Day 1
Lesson
•
3rd Grade

11 questions
Hallway & Bathroom Expectations
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

11 questions
Standard Response Protocol
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

40 questions
Algebra Review Topics
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

4 questions
Exit Ticket 7/29
Quiz
•
8th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

19 questions
Handbook Overview
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Subject-Verb Agreement
Quiz
•
9th Grade