
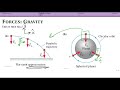
Circular Orbits and Projectile Motion
Interactive Video
•
Physics, Mathematics, Science
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary goal of studying circular orbits in this section?
To discuss the philosophical implications of orbits
To explore the history of circular motion
To apply previously learned concepts to a specific situation
To introduce new concepts in physics
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How does the curvature of Earth affect projectile motion?
It allows projectiles to eventually form orbits
It has no effect on projectile motion
It causes projectiles to move faster
It makes projectiles move in a straight line
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the only force considered in circular orbits?
Electrostatic force
Gravitational force
Magnetic force
Friction
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the context of circular orbits, what does free fall imply?
An object is moving under the influence of gravity alone
An object is stationary
An object is moving upwards
An object is moving in a straight line
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the relationship between centripetal force and orbital speed?
Centripetal force is directly proportional to orbital speed
Centripetal force is unrelated to orbital speed
Centripetal force is directly proportional to the square of orbital speed
Centripetal force is inversely proportional to orbital speed
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What speed is required for an object to maintain a circular orbit close to Earth's surface?
790 meters per second
7.9 kilometers per second
79 kilometers per second
7900 kilometers per second
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why don't we see projectile motion becoming orbits frequently on Earth?
Because of Earth's magnetic field
Due to the high speed required and air resistance
Due to the presence of other planets
Because of the lack of gravitational force
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

6 questions
Graphing Acceleration Explained - Velocity versus Time!
Interactive video
•
10th Grade - University

6 questions
Gravity: Introduction
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
INTERSTELLAR: Is It Deep or Dumb?
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

8 questions
Newton's Second Law and Momentum: Relating Force and Change in Momentum.
Interactive video
•
10th Grade - University
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
Probability Practice
Quiz
•
4th Grade

15 questions
Probability on Number LIne
Quiz
•
4th Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

6 questions
Appropriate Chromebook Usage
Lesson
•
7th Grade

10 questions
Greek Bases tele and phon
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

10 questions
Exit Check 3.3 - Universal Gravitation
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Exit Check 3.4 - Moon's Orbit
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Exit Check 3.5 - Earth's Orbit
Quiz
•
9th Grade

22 questions
Waves
Quiz
•
KG - University

21 questions
EM Spectrum
Quiz
•
6th - 9th Grade

20 questions
Position vs. Time Graphs
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Exploring the Properties of Waves
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

14 questions
Bill Nye Waves
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade