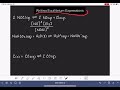
Equilibrium Expressions and KC Values
Interactive Video
•
Chemistry, Science, Mathematics
•
10th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the difference between K and Q in equilibrium expressions?
K is for reactants, while Q is for products.
K is used for concentrations at equilibrium, while Q is for any concentrations.
K is for gases only, while Q is for liquids.
K is a constant, while Q varies with temperature.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How is the KC value calculated in equilibrium expressions?
By using the pressure of gases.
By using the temperature of the reaction.
By using the molarity of reactants and products.
By using the volume of the container.
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the role of stoichiometric coefficients in equilibrium expressions?
They are ignored in the expression.
They are subtracted from the expression.
They are used as exponents in the expression.
They are added to the expression.
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why are pure liquids excluded from equilibrium expressions?
They are always in excess.
They have a constant concentration.
They do not have a defined molarity.
They react too quickly.
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why can't pure solids be included in equilibrium expressions?
They have a fixed volume.
They do not dissolve in water.
They do not have a defined molarity.
They are always reactants.
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the equilibrium expression if the chemical equation is reversed?
The expression is inverted.
The expression is doubled.
The expression is halved.
The expression remains the same.
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How does changing the stoichiometry of a reaction affect the KC value?
It only affects the Q value.
It changes the KC value.
It only affects the reactants.
It does not affect the KC value.
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Solubility Equilibrium Concepts
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
ICE Charts and Equilibrium Concentrations
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Concentration change and equilibrium
Interactive video
•
10th Grade - University

11 questions
Equilibrium in Chemical Reactions
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Predicting direction of reaction
Interactive video
•
10th Grade - University

11 questions
Equilibrium Concentrations and ICE Method
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Equilibrium and Quadratic Equations
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Equilibrium and Equilibrium Constants Quiz
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Nouns, nouns, nouns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
Appointment Passes Review
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

11 questions
All about me
Quiz
•
Professional Development

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

20 questions
Grammar Review
Quiz
•
6th - 9th Grade
Discover more resources for Chemistry

20 questions
Lab Safety and Lab Equipment
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

21 questions
Lab Safety
Quiz
•
10th Grade

12 questions
Significant figures
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Metric Conversions
Quiz
•
11th Grade

30 questions
Aca Nuclear Chemistry
Quiz
•
10th Grade

16 questions
Counting Sig Figs
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Atomic Structure
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Significant Figures
Quiz
•
10th - 11th Grade