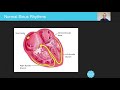
Understanding Sinus Rhythm and ECG
Interactive Video
•
Biology, Science, Health
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary function of the heart's electrical conduction system?
To pump blood throughout the body
To generate electrical impulses for heartbeats
To filter blood
To regulate blood pressure
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Where does the electrical conduction system of the heart begin?
Atrioventricular node
Bundle of His
Sinoatrial node
Purkinje fibers
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the sinoatrial node commonly known as?
The heart's pacemaker
The heart's valve
The heart's filter
The heart's muscle
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which wave on an ECG represents atrial depolarization?
QRS wave
T wave
P wave
U wave
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the typical range of beats per minute for a normal sinus rhythm at rest?
60 to 80 beats per minute
40 to 60 beats per minute
100 to 120 beats per minute
80 to 100 beats per minute
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does the presence of a P wave on an ECG indicate?
Ventricular contraction
Atrial contraction
Heart failure
Heart relaxation
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens when the electrical impulse moves across both atria?
The heart stops
The heart rate decreases
The atria contract
The ventricles contract
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

6 questions
Electrical Conduction System of the Heart Quiz
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Cardiovascular System Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

8 questions
Atrial Fibrillation Treatment and Symptoms
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
ECG Interpretation and Heart Function
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
ECG Interpretation and Heart Activity
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
The Anatomy and Function of the Human Heart
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
ECG/EKG Waveform and Heart Function
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Cardiac Physiology Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
SR&R 2025-2026 Practice Quiz
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

30 questions
Review of Grade Level Rules WJH
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

6 questions
PRIDE in the Hallways and Bathrooms
Lesson
•
12th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Nouns, nouns, nouns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

11 questions
All about me
Quiz
•
Professional Development

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

20 questions
Biomolecules
Quiz
•
9th Grade

22 questions
Macromolecules
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Macromolecules
Quiz
•
9th Grade

19 questions
Scientific Method
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Scientific method
Interactive video
•
9th Grade

18 questions
anatomical planes of the body and directions
Quiz
•
10th Grade

18 questions
Lab Safety
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Biomolecules
Quiz
•
9th Grade