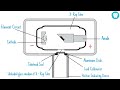
X-ray Tube Components and Functions
Interactive Video
•
Physics, Science, Chemistry
•
9th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the approximate length of the X-ray tube used in dentistry?
15 centimeters
25 centimeters
20 centimeters
10 centimeters
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which component of the X-ray tube is responsible for focusing the electron beam?
Anode
Filament
Focusing cup
Lead collimator
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What material is the filament in the cathode made of?
Tungsten
Aluminum
Molybdenum
Copper
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary function of the anode in the X-ray tube?
To produce X-rays
To focus the electron beam
To generate electrons
To dissipate heat
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which property is NOT essential for the target material in the anode?
Low melting point
High atomic number
High thermal conductivity
Low vapor pressure
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the main reason tungsten is used as the target material in the anode?
Low cost
High atomic number
Easy to mold
High electrical conductivity
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the focal spot in an X-ray tube?
The area where electrons are absorbed and X-rays are generated
The area where X-rays are absorbed
The area where heat is dissipated
The area where electrons are generated
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Introduction to Image Formation Using Mirrors
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
X-ray Tube Components and Functions
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Bremsstrahlung and Characteristic Radiation Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
X-ray Production and Functionality
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
X-ray Machine Components and Functions
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
X-Ray Tube Operation and Student Guidance
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
X-ray Production Fundamentals
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Optics and Light Properties
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
SR&R 2025-2026 Practice Quiz
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

30 questions
Review of Grade Level Rules WJH
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

6 questions
PRIDE in the Hallways and Bathrooms
Lesson
•
12th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Nouns, nouns, nouns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

11 questions
All about me
Quiz
•
Professional Development

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

20 questions
Position vs. Time Graphs
Quiz
•
9th Grade

6 questions
Distance and Displacement
Lesson
•
10th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Distance & Displacement
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Warm Up Review Motion Graphs, Velocity, Speed
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Exit Check 2.4 - 2nd Law Graphs
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Using Scalar and Vector Quantities
Quiz
•
8th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Heat Transfer
Quiz
•
10th Grade