
Bohr Model and Atomic Emission
Interactive Video
•
Chemistry
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What does the Bohr model compare the atom to?
A crystal lattice
A molecule
A solar system
A galaxy
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the Bohr model, what happens when an electron absorbs a photon?
It emits light
It jumps to a higher energy level
It moves to a lower energy level
It remains in the same energy level
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the ground state of an atom?
The lowest energy level
The highest energy level
A state with no electrons
An unstable state
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens when an electron falls to a lower energy level?
It becomes a proton
It absorbs a photon
It emits a photon
It gains energy
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
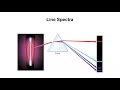
What type of light is emitted when an electron in hydrogen falls from the sixth to the second energy level?
Visible light
X-ray
Ultraviolet
Infrared
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What color of light is emitted when an electron falls from the third to the second energy level in hydrogen?
Violet
Green
Blue
Red
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why do different elements emit different colors of light?
They have different numbers of protons
They have unique energy levels
They have different atomic masses
They have different electron spins
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Ionic Bonds and Electron Transfer
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
CHO+ Molecular Geometry and Bonding
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Isotopes and Ions Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Basic Chemistry Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 11th Grade

6 questions
CLEAN : Separatists take adandoned Ukrainian tanks in Komsomolske
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Algebra and Geometry Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

7 questions
Lewis Structures and Electron Pairs
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
CLEAN : Costa Rica eyes green hydrogen technology
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

10 questions
Probability Practice
Quiz
•
4th Grade

15 questions
Probability on Number LIne
Quiz
•
4th Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

6 questions
Appropriate Chromebook Usage
Lesson
•
7th Grade

10 questions
Greek Bases tele and phon
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade
Discover more resources for Chemistry

20 questions
Predicting Products
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Balancing Chemical Equations
Lesson
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Types of Chemical Reactions
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

19 questions
Stoichiometry, % yield, Limiting Reactants
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Types of Chemical Reactions
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Ionic and Covalent Bonding Concepts
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

7 questions
GCSE Chemistry - Balancing Chemical Equations #4
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

12 questions
Percent Yield
Quiz
•
10th Grade