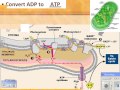
Photosynthesis: Light-Dependent Reactions
Interactive Video
•
Biology
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What are the two main stages of photosynthesis?
Glycolysis and Krebs cycle
Oxidative phosphorylation and photolysis
Light-dependent reactions and Calvin cycle
Electron transport chain and fermentation
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary purpose of the light-dependent reactions?
To fix carbon dioxide
To convert light energy into chemical energy
To release carbon dioxide
To produce glucose directly
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the initial source of electrons in the light-dependent reactions?
Carbon dioxide
Oxygen
Water
Glucose
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to water molecules during the light-dependent reactions?
They are converted into glucose
They are stored in the chloroplast
They are split to release oxygen, electrons, and protons
They are used to fix carbon dioxide
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which molecule acts as an electron carrier in photosynthesis?
Glucose
FADH2
ATP
NADPH
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the main function of NADPH in photosynthesis?
To act as a structural component of chloroplasts
To carry high-energy electrons for the Calvin cycle
To absorb sunlight
To directly produce ATP
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the role of the electron transport chain in photosynthesis?
To directly produce glucose
To transport water molecules
To break down glucose
To create a proton gradient for ATP synthesis
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Light-Dependent Reactions of Photosynthesis
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Photosynthesis Concepts and Processes
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Photosynthesis Concepts and Processes
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Calvin Cycle and Photosynthesis Concepts
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Photosynthesis Processes and Functions
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Photosynthesis Unveiled: The Process That Powers Life on Earth
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Photosynthesis Concepts and Processes
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Hallway & Bathroom Expectations
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

20 questions
PBIS-HGMS
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

10 questions
"LAST STOP ON MARKET STREET" Vocabulary Quiz
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

19 questions
Fractions to Decimals and Decimals to Fractions
Quiz
•
6th Grade

16 questions
Logic and Venn Diagrams
Quiz
•
12th Grade

15 questions
Compare and Order Decimals
Quiz
•
4th - 5th Grade

20 questions
Simplifying Fractions
Quiz
•
6th Grade

20 questions
Multiplication facts 1-12
Quiz
•
2nd - 3rd Grade