Cell Transport and Membrane Functions
Interactive Video
•
Biology
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary function of the cell membrane?
To synthesize proteins
To store genetic information
To produce energy for the cell
To control what enters and exits the cell
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which part of the phospholipid is attracted to water?
Cholesterol
Phosphate head
Protein channels
Lipid legs
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In passive transport, molecules move from areas of _____ concentration to areas of _____ concentration.
none; some
equal; equal
high; low
low; high
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
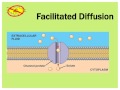
What is the role of protein channels in facilitated diffusion?
To break down molecules
To act as passageways for large or polar molecules
To provide energy for transport
To store molecules
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
During osmosis, water moves towards the _____ side of the membrane.
hypotonic
neutral
hypertonic
isotonic
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the example given, if the outside concentration is 1.5 grams per liter and the inside is 1 gram per liter, where will the solute move?
It will move both ways equally
It will not move
From outside to inside
From inside to outside
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which process involves the cell using energy to engulf solid food?
Exocytosis
Phagocytosis
Pinocytosis
Diffusion
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

8 questions
10 Apocalyptic Natural Disasters That Are Waiting To Happen
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
CLEAN: Low-key commemoration five years after London bombings
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
CLEAN : Strikers urged to remain steadfast at S Africa platinum mine
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
CLEAN : Suicide blasts kill 10 in NE Nigeria
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
CLEAN : Root causes of Mideast conflict
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
CLEAN : Family pay tribute to S.African jazz legend Hugh Masekela
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
US President Roosevelt addresses joint session of Congress asking to declare war against Japan
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

2 questions
GCSE Physics - Biofuels #12
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
4th Grade

20 questions
Figurative Language Review
Quiz
•
6th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

20 questions
Cell Organelles
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Cell Organelles
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
DNA & Protein Synthesis
Quiz
•
9th Grade

7 questions
Amoeba Sisters Dihybrid Cross Punnett Square
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

25 questions
photosynthesis and cellular respiration
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Human Body Systems
Quiz
•
9th Grade

19 questions
Natural Selection
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Pedigree Practice
Quiz
•
9th Grade