
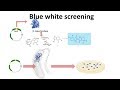
Recombinant DNA Techniques and Screening
Interactive Video
•
Biology
•
10th - 11th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary purpose of blue-white screening in molecular biology?
To select recombinant colonies
To enhance plasmid replication
To identify antibiotic-resistant bacteria
To measure bacterial growth rate
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which step in the cloning workflow involves the use of restriction enzymes?
Selection of recombinant colonies
Ligation of plasmids
Transformation into bacteria
Restriction digestion of vectors and genes
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why is antibiotic resistance important in the cloning process?
It enhances the growth rate of bacteria
It helps in identifying self-ligated plasmids
It allows bacteria to survive in antibiotic-containing media
It increases the transformation efficiency
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What problem does the use of screenable markers, like the lacZ gene, address?
Increasing bacterial growth rate
Antibiotic resistance
Low transformation efficiency
Distinguishing between recombinant and self-ligated plasmids
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the lacZ gene when a gene of interest is inserted into its locus?
It enhances the production of beta-galactosidase
It remains unaffected
It increases the transformation efficiency
It gets inactivated, preventing beta-galactosidase production
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What color do colonies appear if they contain recombinant plasmids?
Blue
Red
White
Green
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the role of beta-galactosidase in blue-white screening?
It provides antibiotic resistance
It converts X-gal into a colored product
It enhances plasmid replication
It increases bacterial growth rate
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

8 questions
Aging and Genetics in Biology
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

10 questions
CRISPR Technology and Its Implications
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Genetic Engineering in Agriculture
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Sordaria Genetics and Meiosis Concepts
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Genetic Editing and Technological Evolution
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Lupus Diagnosis and Evaluation Concepts
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Molecular Biology Concepts Assessment
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Claims and Definitions
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

8 questions
Spartan Way - Classroom Responsible
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

14 questions
Boundaries & Healthy Relationships
Lesson
•
6th - 8th Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

3 questions
Integrity and Your Health
Lesson
•
6th - 8th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

9 questions
FOREST Perception
Lesson
•
KG

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade
Discover more resources for Biology

18 questions
Mendelian Genetics
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

21 questions
Cell Cycle and mitosis
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Food Chains and Food Webs
Quiz
•
7th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Food Webs and Energy Pyramids
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

55 questions
Category2 SPRING 2026 - STAAR 2.0
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

72 questions
#Category 4 - STAAR 2.0
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

73 questions
#Category 1 - STAAR 2.0
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

16 questions
Punnett Square
Quiz
•
7th - 10th Grade