Geologic Cross-Section Principles
Interactive Video
•
Geology
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary purpose of geologic cross-sections?
To predict future volcanic eruptions
To interpret past geologic conditions and relative ages
To measure the current temperature of the Earth's core
To create three-dimensional models of the Earth's surface
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following is NOT a type of geologic event?
Metamorphic transformation
Magnetic field reversal
Igneous formation
Sedimentary deposition
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is an unconformity in geology?
A type of fault
A type of sedimentary rock
A period of non-deposition or missing time
A volcanic eruption
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which principle helps determine that the oldest layers are at the bottom in a sequence of sedimentary rocks?
Principle of Lateral Continuity
Principle of Original Horizontality
Principle of Superposition
Principle of Cross-Cutting Relationships
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
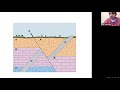
In the example of a geologic cross-section, what does the feature labeled 'D' represent?
A sedimentary layer
An igneous dike
A metamorphic rock
A fault line
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the correct order of events from oldest to youngest in the given geologic cross-section example?
E, D, C, B, A
D, E, A, B, C
C, B, A, D, E
A, B, C, D, E
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which principle is used to determine that 'D' is older than 'E' in the cross-section?
Principle of Superposition
Principle of Cross-Cutting Relationships
Principle of Lateral Continuity
Principle of Original Horizontality
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

54 questions
Analyzing Line Graphs & Tables
Quiz
•
4th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
4th Grade
Discover more resources for Geology

20 questions
El Verbo IR Practice
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
-AR -ER -IR present tense
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Understanding Meiosis
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

20 questions
Graphing Inequalities on a Number Line
Quiz
•
6th - 9th Grade

15 questions
Making Inferences
Quiz
•
7th - 12th Grade

18 questions
SAT Prep: Ratios, Proportions, & Percents
Quiz
•
9th - 10th Grade

15 questions
Main Idea and Supporting Details.
Quiz
•
4th - 11th Grade

12 questions
Exponential Growth and Decay
Quiz
•
9th Grade