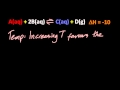
Le Chatelier's Principle and Equilibrium
Interactive Video
•
Chemistry
•
10th - 12th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary purpose of Le Chatelier's Principle in equilibrium systems?
To calculate the exact concentration of reactants
To understand how systems respond to stress
To determine the speed of reactions
To predict the color change in reactions
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How does increasing the concentration of a reactant affect the equilibrium position?
It has no effect on the equilibrium
It shifts the equilibrium to the right
It stops the reaction completely
It shifts the equilibrium to the left
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How does removing a reactant affect the equilibrium position?
It shifts the equilibrium to the left
It shifts the equilibrium to the right
It has no effect on the equilibrium
It increases the reaction rate
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to the equilibrium when the pressure is increased in a system with gases?
The equilibrium shifts to the side with more gas particles
The reaction stops
The equilibrium shifts to the side with fewer gas particles
The equilibrium remains unchanged
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the result of increasing pressure in a reaction with equal moles of gas on both sides?
The equilibrium shifts to the left
The reaction stops
The equilibrium shifts to the right
The equilibrium remains unchanged
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
If a system at equilibrium is heated, which side of the reaction is favored?
The side that releases heat (exothermic)
The side with more products
The side that absorbs heat (endothermic)
The side with more reactants
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In a reaction where the forward reaction is exothermic, what happens when the temperature is increased?
The equilibrium remains unchanged
The reaction stops
The equilibrium shifts to the left
The equilibrium shifts to the right
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Popular Resources on Wayground

8 questions
2 Step Word Problems
Quiz
•
KG - University

20 questions
Comparing Fractions
Quiz
•
4th Grade

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

10 questions
Latin Bases claus(clois,clos, clud, clus) and ped
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

7 questions
The Story of Books
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade
Discover more resources for Chemistry

20 questions
Unit 7 Chemical Reactions
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Practice: E-Con, Orbital Notation, Noble Gas Notation
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Stoichiometry Practice
Quiz
•
10th Grade

22 questions
Periodic Trends Freshman
Quiz
•
10th Grade

23 questions
Unit 7 Chemical Reactions
Quiz
•
10th Grade

17 questions
Reaction Rates
Quiz
•
11th Grade

20 questions
Periodic Trends
Quiz
•
10th Grade