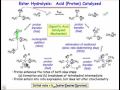
Ester Hydrolysis Reaction Mechanisms
Interactive Video
•
Chemistry
•
11th - 12th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the primary focus of comparing uncatalyzed and catalyzed reactions in the context of ester hydrolysis?
To determine the final products of the reaction
To understand how the catalyst appears in the rate law
To calculate the energy released in the reaction
To measure the temperature change during the reaction
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the uncatalyzed ester hydrolysis reaction, what is the role of the nucleophile?
To add to a polarized pi bond
To act as a leaving group
To stabilize the intermediate
To donate a proton
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which step is considered the rate-determining step in the uncatalyzed ester hydrolysis reaction?
Nucleophile addition
Proton transfer
Beta elimination
Formation of the carboxylic acid
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How is the concentration of the tetrahedral intermediate accounted for in the rate law derivation?
By assuming it is constant
By ignoring it completely
By using fast equilibrium assumptions
By direct measurement
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What assumption is made to simplify the reaction and focus on the forward rate?
The reaction is at equilibrium
The reaction is exothermic
The backward reaction is negligible
The catalyst is consumed
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the proton-catalyzed mechanism, what role does the proton play in the reaction?
It stabilizes the final product
It is consumed and not regenerated
It acts as a nucleophile
It enhances the electrophilicity of the carbonyl
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How does the proton affect the rate-determining step in the catalyzed reaction?
It has no effect
It accelerates the beta elimination
It changes the reaction pathway
It slows down the reaction
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Reaction Rates and Isomer Conformations
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Catalysis Concepts and Mechanisms
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Chemical Kinetics and Reaction Energy
Interactive video
•
10th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Enzyme Kinetics and Mechanisms
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Activation Energy and Reaction Rates
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

8 questions
Hydrohalogenation, Hydration, Dihalogenation
Interactive video
•
11th Grade - University

11 questions
Alpha Substitution Reactions Quiz
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade

11 questions
Alpha Halogenation and Related Reactions Quiz
Interactive video
•
11th - 12th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

55 questions
CHS Student Handbook 25-26
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Afterschool Activities & Sports
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

15 questions
PRIDE
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

15 questions
Cool Tool:Chromebook
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Nouns, nouns, nouns
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Bullying
Quiz
•
7th Grade

18 questions
7SS - 30a - Budgeting
Quiz
•
6th - 8th Grade
Discover more resources for Chemistry

20 questions
Lab Safety and Lab Equipment
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Lab Equipment Quiz Chemistry
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Lab Safety
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

8 questions
Metric System
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

40 questions
Lab Safety
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Classification of Matter
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

12 questions
Significant figures
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade