Accuracy and Precision in Experiments
Interactive Video
•
Physics
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the main difference between accuracy and precision?
Accuracy refers to how close results are to the true value, while precision refers to the consistency of results.
Accuracy is about the consistency of results, while precision is about how close results are to the true value.
Accuracy and precision are the same and can be used interchangeably.
Accuracy is only important in physics, while precision is only important in chemistry.
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following is necessary to achieve high accuracy in an experiment?
Using a detailed method and the right equipment.
Using any available equipment without checking its resolution.
Having a large number of random errors.
Ignoring systematic errors.
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is a systematic error?
An error that only occurs in chemistry experiments.
An error caused by human mistakes.
An error that is consistent and affects accuracy.
An error that occurs randomly and affects precision.
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What type of error is most associated with precision?
Instrumental errors
Random errors
Human errors
Systematic errors
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How can random errors be minimized in an experiment?
By using a detailed method and ensuring consistent measurements.
By ignoring them as they do not affect results.
By using faulty equipment.
By increasing the number of systematic errors.
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
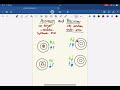
In the dartboard example, what does it mean if the darts are close together but far from the bullseye?
High accuracy, low precision
Low accuracy, high precision
High accuracy, high precision
Low accuracy, low precision
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
In the penalty example, what does it mean if all shots are scored but are all over the place?
Low accuracy, high precision
High accuracy, low precision
Low accuracy, low precision
High accuracy, high precision
Access all questions and much more by creating a free account
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
Already have an account?
Similar Resources on Wayground

11 questions
Refrigeration Cycle Quiz
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Understanding the Senior Tax Break
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Social Security Changes
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Understanding Business Competition
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Keynote Presentation Techniques Quiz
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Tablet Comparison Quiz
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

15 questions
Fractions on a Number Line
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

54 questions
Analyzing Line Graphs & Tables
Quiz
•
4th Grade

22 questions
fractions
Quiz
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Main Idea and Details
Quiz
•
5th Grade

20 questions
Context Clues
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Equivalent Fractions
Quiz
•
4th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

27 questions
Simple Machines and Mechanical Advantage Quiz
Quiz
•
9th Grade

10 questions
Understanding Heat, Thermal Energy, and Temperature
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Newton's Laws of Motion
Quiz
•
10th Grade

10 questions
unit 10 -- electric forces and fields
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

21 questions
Diffraction, Reflection, Refraction
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Position vs. Time and Velocity vs. Time Graphs
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Types of Chemical Reactions
Quiz
•
10th Grade

11 questions
Conservation of Momentum: Physics in Motion Video
Interactive video
•
10th Grade