Fluid Mechanics Concepts and Principles
Interactive Video
•
Physics
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Hard
Patricia Brown
FREE Resource
Read more
10 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which of the following principles is NOT covered in the introduction to fluid mechanics?
Newton's Third Law
Bernoulli's Principle
Archimedes' Principle
Pascal's Principle
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is a key difference between gases and liquids?
Gases have an indefinite volume, liquids have a definite volume.
Liquids are made of rapidly moving particles, gases are not.
Liquids can be compressed easily, gases cannot.
Gases have a definite shape, liquids do not.
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How is mass density defined?
Area divided by volume
Mass divided by area
Volume divided by mass
Mass divided by volume
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which unit is commonly used in physics to measure pressure?
Inches of mercury
Atmosphere
Pounds per square inch
Pascal
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
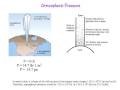
What causes atmospheric pressure?
The heat from the sun
The gravitational pull of the moon
The weight of the air pressing down on Earth's surface
The rotation of the Earth
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why doesn't atmospheric pressure crush your forearm when resting on a table?
Fluids exert pressure in all directions, balancing the forces
Air pressure is only exerted downwards
The table supports the weight of the air
The forearm is too strong to be crushed
7.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to pressure as you dive deeper underwater?
It increases
It remains constant
It fluctuates
It decreases
Create a free account and access millions of resources
Create resources
Host any resource
Get auto-graded reports

Continue with Google

Continue with Email

Continue with Classlink

Continue with Clever
or continue with

Microsoft
%20(1).png)
Apple
Others
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy
Already have an account?
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Honoring the Significance of Veterans Day
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Veterans Day: Facts and Celebrations for Kids
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

19 questions
Veterans Day
Quiz
•
5th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

15 questions
Circuits, Light Energy, and Forces
Quiz
•
5th Grade

6 questions
FOREST Self-Discipline
Lesson
•
1st - 5th Grade

7 questions
Veteran's Day
Interactive video
•
3rd Grade

20 questions
Weekly Prefix check #2
Quiz
•
4th - 7th Grade
Discover more resources for Physics

10 questions
Types of Chemical Reactions
Quiz
•
10th Grade

14 questions
Bill Nye Waves
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

20 questions
Newton's 2nd Law
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

25 questions
Waves-8th Grade Physical Science
Quiz
•
KG - University

14 questions
Work and Power
Lesson
•
10th - 12th Grade

6 questions
Conservation of Energy
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Newton's Third Law
Quiz
•
7th - 11th Grade

20 questions
Calculating Net Force
Quiz
•
6th - 9th Grade