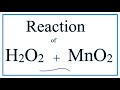
Catalysts and Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide
Interactive Video
•
Chemistry
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Hard
Jackson Turner
FREE Resource
Read more
6 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What are the products formed when hydrogen peroxide decomposes?
Hydrogen and water
Hydrogen and oxygen
Water and oxygen
Water and carbon dioxide
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is observed when hydrogen peroxide is applied to a wound?
It evaporates quickly
It produces bubbles of oxygen
It forms a solid layer
It turns blue
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What is the role of a catalyst in a chemical reaction?
It is consumed in the reaction
It slows down the reaction
It speeds up the reaction without being consumed
It changes the products of the reaction
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which enzyme in the blood acts as a catalyst for the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide?
Lipase
Protease
Catalase
Amylase
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Why is MnO2 written above the reaction arrow in the decomposition of H2O2?
Because it is a reactant
Because it is a product
Because it is a catalyst and remains unchanged
Because it is an inhibitor
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What happens to MnO2 after the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide?
It is converted into oxygen
It is converted into water
It is consumed in the reaction
It remains unchanged
Similar Resources on Wayground

9 questions
Sodium Peroxide Formation and Balancing
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

7 questions
Manganese Oxide Compounds and Properties
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

10 questions
Hydrogen Peroxide Properties and Structure
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Balancing Chemical Equations and Reactions
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
Manganese 3-Nitrate Molar Mass
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
Manganese and Sulfide Compounds
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

6 questions
Decomposition Reactions in Chemistry
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade

11 questions
Science Made Simple: Rate of Reaction Quiz
Interactive video
•
9th - 10th Grade
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Video Games
Quiz
•
6th - 12th Grade

10 questions
Lab Safety Procedures and Guidelines
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

10 questions
UPDATED FOREST Kindness 9-22
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade

22 questions
Adding Integers
Quiz
•
6th Grade

15 questions
Subtracting Integers
Quiz
•
7th Grade

20 questions
US Constitution Quiz
Quiz
•
11th Grade

10 questions
Exploring Digital Citizenship Essentials
Interactive video
•
6th - 10th Grade
Discover more resources for Chemistry

15 questions
Isotopes/structure of an atom
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Atomic Structure
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

20 questions
COUNTING ATOMS
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Periodic Trends
Quiz
•
10th Grade

15 questions
Exploring the Unique Properties of Water
Interactive video
•
9th - 12th Grade

17 questions
CHemistry Unit 7 Dimensional Analysis Practice
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

47 questions
Unit #4 Electron KAP Test Review
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

7 questions
Elements, Compounds, Mixtures
Lesson
•
9th - 12th Grade