Polarity and Structure of SO2
Interactive Video
•
Chemistry
•
9th - 10th Grade
•
Practice Problem
•
Hard
Sophia Harris
FREE Resource
Read more
6 questions
Show all answers
1.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What aspect of the SO2 molecule's Lewis structure suggests it might be polar?
Symmetry on the top and bottom
Symmetry on the left and right
Presence of a lone pair of electrons
Absence of double bonds
2.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
How does the three-dimensional structure of SO2 differ from a straight molecule?
It is bent
It is planar
It is linear
It is tetrahedral
3.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What color represents sulfur in the three-dimensional model of SO2?
Red
Blue
Green
Yellow
4.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
What role do the valence electrons play in the polarity of SO2?
They make the molecule nonpolar
They contribute to the molecule's bent shape
They are not present in the molecule
They neutralize the molecule
5.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
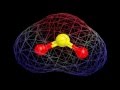
What does the molecular surface analysis of SO2 reveal?
The molecule is nonpolar
The molecule has no charge
The molecule has two poles
The molecule is symmetrical
6.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION
30 sec • 1 pt
Which area of the SO2 molecule is more positive according to the molecular surface analysis?
The blue area
The yellow area
The red area
The green area
Popular Resources on Wayground

10 questions
Forest Self-Management
Lesson
•
1st - 5th Grade

25 questions
Multiplication Facts
Quiz
•
5th Grade

30 questions
Thanksgiving Trivia
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

30 questions
Thanksgiving Trivia
Quiz
•
6th Grade

11 questions
Would You Rather - Thanksgiving
Lesson
•
KG - 12th Grade

48 questions
The Eagle Way
Quiz
•
6th Grade

10 questions
Identifying equations
Quiz
•
KG - University

10 questions
Thanksgiving
Lesson
•
5th - 7th Grade
Discover more resources for Chemistry

88 questions
Test Review
Quiz
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Unit 3, Quiz #6 Practice - Types of Covalent
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

22 questions
Unit 2 Part 1 Rumble
Quiz
•
10th Grade

20 questions
Molar Mass
Quiz
•
9th - 12th Grade

17 questions
Protein Synthesis (Protein Synthesis)
Interactive video
•
9th Grade

20 questions
Electron Configuration
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade

15 questions
Balancing Chemical Equations
Quiz
•
10th - 12th Grade